Schrodinger Wave Equation
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
(1) Schrodinger wave equation is given by Erwin Schrödinger in 1926 and based on dual nature of electron.
(2) In it electron is described as a three dimensional wave in the electric field of a positively charged nucleus.
(3) The probability of finding an electron at any point around the nucleus can be determined by the help of Schrodinger wave equation which is, \[\frac{\partial {}^{2}\Psi }{\partial x{}^{2}}+\,\frac{\partial {}^{2}\Psi }{\partial y{}^{2}}+\,\frac{\partial {}^{2}\Psi }{\partial z{}^{2}}+\frac{8\pi {}^{2}m}{h{}^{2}}(E-V)\,\Psi =0\]
Where \[x,\,y\] and z are the 3 space co-ordinates, m = mass of electron, h = Planck?s constant, E = Total energy, V = potential energy of electron, \[\Psi \]= amplitude of wave also called as wave function, \[\partial \] = for an infinitesimal change.
(4) The Schrodinger wave equation can also be written as, \[\nabla {}^{2}\Psi +\frac{8\pi {}^{2}m}{h{}^{2}}(E-V)\,\,\Psi =0\]
Where \[\nabla \]= laplacian operator.
(5) Physical significance of \[\Psi \] and \[\Psi {}^{2}\]
(i) The wave function \[\Psi \] represents the amplitude of the electron wave. The amplitude \[\Psi \] is thus a function of space co-ordinates and time i.e. \[\Psi =\Psi (x,\,y,\,\,z......times)\]
(ii) For a single particle, the square of the wave function \[(\Psi {}^{2})\] at any point is proportional to the probability of finding the particle at that point.
(iii) If \[\Psi {}^{2}\] is maximum than probability of finding \[{{e}^{-}}\] is maximum around nucleus and the place where probability of finding \[e{}^{-}\] is maximum is called electron density, electron cloud or an atomic orbital. It is different from the Bohr?s orbit.
(iv) The solution of this equation provides a set of number called quantum numbers which describe specific or definite energy state of the electron in atom and information about the shapes and orientations of the most probable distribution of electrons around the nucleus.
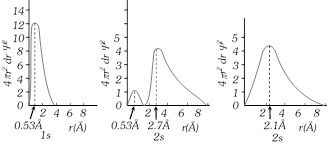
Radial probability distribution curves : Radial probability is \[R=4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr{{\psi }^{2}}.\] The plats of \[R\] distance from nucleus as follows
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
