Sources Of Business Finance (Notes)
Category : 11th Class
Sources of Business Finance
Facts that Matter
- No business can be started, run or expanded without finance.
- There are many sources of finance. Each source has its own merits and demerits.
- Business needs to choose right source of finance to make the best use of it.
Business Finance
It refers to the money required for carrying out business activities.
Significance of Business Finance
- Business is concerned with production and distribution of goods and services for the satisfaction of needs of society.
- No business can be carried without availability of adequate funds.
- As soon as a decision is taken to start a business, requirement of funds initiates.
- Finance is called 'life blood of a business'.
- It is very important to assess financial needs of the organization and the identification of various sources of finance.
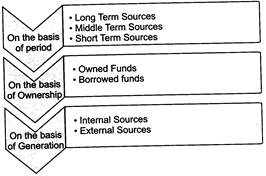
Classification of Sources of Funds
Overall financial requirements can be classified into:
Ø Fixed Capital Requirements
Ø Working Capital Requirements.
- Fixed capital is a capital used to buy land and building, plant and machinery, furniture and fixtures etc.
- Working capital requirements refer to capital required for meeting running expenses of business.
On the basis of period, funds can be categorized into
Ø Long term sources
Ø Middle term sources
Ø Short term sources
- Long term sources fulfil the financial requirements of an enterprise for a period exceeding 5 years.
- Middle term sources fulfil the financial requirements of an enterprise for a period of one to five years.
- Short term sources fulfil the financial requirements of an enterprise for a period not exceeding one year.
On the basis of ownership, funds can be classified into
Ø Owner's Funds
Ø Borrowed Funds
- Owner's funds are the funds that are provided by the owners of an enterprise.
- Borrowed funds refer to the funds raised through borrowings.
Equity Shares
Equity shares are those shares which do not carry any special or preferential rights in respect of payment of annual dividend and repayment of capital.
Merits of Equity Shares
- It is ideal for adventurous investors
- There is no obligation as to dividend
- It provides credit standard
- It is a source of fixed capital
- It creates no charge on assets
- It creates democratic management
- It has a small nominal value
Limitations of Equity Shares
- There is risk of fluctuating returns
- It leads to dilution of capital
- It has many legal formalities
- Equity shares capital has high cost of capital
- It suffers from the danger of over-capitalisation
Preference Shares
Preference shares are those shares, which enjoy preferential right in payment of dividend and repayment of capital.
Merits of Preference Shares
- It gives reasonable safety of returns.
- Repayment of principal amount is ensured.
- There is no interference in management.
- Trading on equity is allowed.
- It creates no charge on assets.
Limitations of Preference Shares
- It has limited appeal.
- It dilutes claim of equity shareholders.
- It is unreliable and gives low returns.
- It has no tax benefits.
Retained Earnings
Retained earnings refer to that part of profits which is kept as reserve for use in the future.
Merits of Retained Earnings
- It is a dependable source.
- It is economical.
- It has more freedom.
- It has ability to absorb shocks in business.
- It enhances market value of shares.
- It brings stability of dividend.
Limitations of Retained Earnings
- It creates dissatisfaction among shareholders.
- It is uncertain.
- It ignores opportunity cost.
- There is danger of over-capitalisation.
Global Depository Receipts (GDRs)
GDR is an instrument issued by a company to raise funds in some foreign currency and is listed and traded on a foreign stock exchange.
American Depository Receipts (ADRs)
The depository receipts issued by the company in USA are called American Depository Receipts.
Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs)
IDR is an instrument in the form of a depository receipt created by the Indian depository in India against the underlying equity shares of the issuing company.
Debentures/ Bonds
A debenture is a document or certificate, which is issued under the common seal of the company, acknowledging its debt to the holder at given terms and conditions.
Merits of Debentures
- It is ideal for safe investors.
- There is no loss of control.
- It has flexibility.
- It is economical.
- It is suitable during stable earnings.
- It has tax benefits.
- It leads to trading on equity.
Limitations of Debentures
- It is a permanent burden of interest.
- It has adverse impact on borrowing capacity.
- It has repayment obligation.
- It creates charge on assets.
Loans from Financial Institutions
These institutions provide finance to business organizations and are suitable to raise large funds for long-term.
Merits of Financial Institutions
- It provides medium and long-term finance.
- It gives assistance in business.
- It is a source of goodwill.
- It has easy repayment scheme.
- It provides finance even during depression.
Limitations of Financial Institutions
- It has difficult procedure.
- It has restrictive clauses.
- It creates interference in management.
Loans from Commercial Banks
Commercial bank is an institution which performs the function of accepting deposits, granting loans and making investments, with the aim of earning profits.
Merits of Commercial Banks
- It is economical.
- It maintains business secrecy.
- It has less formalities.
- It is a flexible source.
Limitations of Commercial Banks
- It provides short-term financing.
- It has difficult procedure.
- It has restrictive clauses.
Public Deposits
Public deposits are the deposits raised by organizations directly from the public.
Merits of Public Deposits
- It has a simple procedure.
- It leads to no loss of control.
- It is economical.
- It creates no change over assets.
Limitations of Public Deposits
- It is not suitable for new companies.
- It is not suitable for long term financing.
- It is not a reliable source.
- It can provide limited funds.
Trade Credit
Trade credit is the credit extended by one trader to another for the purchase of goods and services.
Merits of Trade Credit
- It is a convenient source.
- It promotes sales.
- It helps in raising inventory level.
- It has ready availability.
- It creates no charge on assets
Limitations of Trade Credit
- It has risk of overtrading.
- It is costly.
- It can provide limited funds.
Inter-Corporate Deposits (ICD)
Inter-Corporate Deposits (ICD) is an unsecured borrowing by companies (corporate) from other corporate entities registered under the Companies Act, 1956.
Merits of Inter-Corporate Deposits
- It is free from bureaucratic and legal problems.
- It helps in meeting working capital requirements.
- Secrecy is maintained.
Demerits of Inter-Corporate Deposits
- It is not suitable for long-term financing.
- It has high interest rates.
- It is unsecured.
Words that Matter
- Business Finance: Business finance refers to the money required for carrying out business activities. It is concerned with acquisition of funds, use of funds and distribution of profits by a business enterprise.
- Owner's Funds: Owner's funds are the funds provided by the owner of the business enterprise.
- Factoring: Factoring is a financial service under which the factor discount the bills of exchange of the clients and collects his debts and also provides him information on credit worthiness of perspective client. He charges fees for the services rendered.
- Equity Shares: Equity shares are those shares which do not carry any special or preferential rights in respect of payment of annual dividend and repayment of capital.
- Preference Shares: Preference shares are those shares, which enjoy certain priorities regarding the payment of dividend at a fixed rate and return of the investment (capital).
- Global Depository Receipts(GDRs): GDR is an instrument issued by a company to raise funds in some foreign currency and is listed and traded on a foreign stock exchange.
- Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs): IDR is an instrument in the form of a depository receipt created by the Indian depository in India against the underlying equity shares of the issuing company.
- Borrowed Funds: Borrowed funds are the funds raised through loans or borrowings.
- Debenture: A debenture is a document or certificate, which is issued under the common seal of the company, acknowledging its debt to the holder at given terms and conditions.
- Public Deposits: Public deposits are the deposits raised by organizations directly from the public
- Trade Credit: Trade credit is the credit extended by one trader to another for the purchase of goods mid services.
- Retained Earnings: A company generally does not distribute all its earnings amongst shareholders in the form of dividend. A portion of the net earnings may be retained in the business of use in future. These are called retained earnings.
- Zero Interest Debenture (ZID): Zero interest debentures do not carry any explicit rate of interest. But they are issued at discount and redeemed at a premium or at par. It is the return on the debenture.
- Inter-Corporate Deposits (ICD): Inter-Corporate Deposit (ICD) is an unsecured borrowing by companies (corporate) from other corporate entities registered under the Companies Act, 1956.
- Commercial bank: Commercial bank is an institution which performs the functions of accepting deposits, granting loans and making investments, with the aim of earning profits.
- Lease Financing: A lease is a contractual agreement, in which the owner of the asset grants the other party the right to use the asset in return for a periodic payment, but retains the title over the property.
- Commercial Paper: Commercial paper is an unsecured promissory note issued by a firm to raise funds for a short period, varying from 90 days to 364 days.

