Class Amphibia - The Vertebrates With Dual Life
Category : 11th Class
(Gk. Amphi = both; bios = Life)
General characters
(1) Aquatic or semi aquatic (freshwater), air and water breathing, carnivorous, cold–blooded, oviparous, tetrapod vertebrates.
(2) Head distinct, trunk elongated. Neck and tail may be present or absent.
(3) Limbs usually 2 pairs (tetrapod), some limb less Toes 4-5 (pentadactyle) or less. Paired fins absent. Median fins, if present, without fin rays.
(4) Skin soft, moist and glandular. Pigment cells (chromatophores) present.
(5) Exoskeleton absent. Digits claw less. Some with concealed dermal scales.
(6) Endoskeleton mostly bony. Notochord does not persist. Skull with 2 occipital condyles. i.e. Dicondylic skull.
(7) Mouth large. Upper or both jaws with small homodont teeth. Tongue often protrusible. Alimentary canal terminates into cloaca.
(8) Respiration by lungs, skin and mouth lining. Larvae with external gills which may persist in some aquatic adults.
(9) Heart 3–chambered (2 auricles + 1 ventricle). Sinus venosus present. Aortic arches 1-3 pairs. Renal and hepatic portal systems well developed Erythrocytes large, oval and nucleated. Body temperature variable (poikilothermous).
(10) Kidneys mesonephric. Urinary bladder large. Urinary ducts open into cloaca. Excretion ureotelic.
(11) Brain poorly developed. Cranial nerves 10 pairs.
(12) Nostrils connected to buccal cavity. Middle ear with a single rod-like ossicle, columella. Larval forms and some aquatic adults with lateral line system.
(13) Sexes separate. Male without copulatory organ Gonoducts open into cloaca. Fertilization mostly external. Females mostly oviparous.
(14) Development indirect. Cleavage holoblastic but unequal. No extra–embryonic membranes. Larva a tadpole which metamorphoses into adult.
Classification of Amphibia : The living amphibians belong to only 2,500 species, a very much smaller number than that of other principal classes of vertebrates. Ranging from mid-Palaeozoic (Devonian) to early Mesozoic (Triassic). They dominated the World during Carboniferous, but most of them have become extinct since long. The classification most generally followed nowadays was provided by G. Kingsley Noble (1924).
(a) Subclass I. Stegocephalia (Extinct) : Limbs pentadactyle. Skin with scales and bony plates. Skull with a solid bony roof leaving openings for eyes and nostrils. Permian to Triassic.
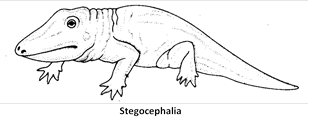
Order 1. Labyrinthodontia : Oldest known tetrapods called stem Amphibia. Carboniferous to Triassic.
Example : Eryops.
Order 2. Phyllospondyli : Small salamander-like. Carboniferous to permian.
Example : Branchiosaurs (Ichthyostega).
Order 3. Lepospondyli – Small salamander or eel-like.Carboniferous to Permian.
Examples – Diplocaulus, Lysorophus.
(b) Subclass II. Lissamphibia (living) : Modern Amphibia lacking dermal bony skeleton. Teeth small, simple.
Order 1. Gymnophiona or Apoda : (Gk. gymnos = naked ; ophioneos = serpet-like).
(1) Limb less, blind, elongated worm like, burrowing tropical forms known as caecilians or blind worms.
(2) Tail short or absent, cloaca terminal.
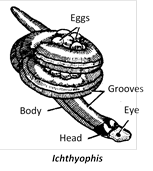
(3) In some dermal scales embedded in skin which is transversely wrinkled.
(4) Skull compact, roofed with bone.
(5) Limb girdle absent.
(6) Males have protrusible copulatory organs,
Examples : Ichthyophis, Uroaeoryphlus, Rhinatremam, Typhlonectes.
Order 2. Urodela or Caudata : (Gk. Ura = tail ; delos = visible) or (L. = cauda = tail).
(1) Lizard-like amphi- bians with a distinct tail.
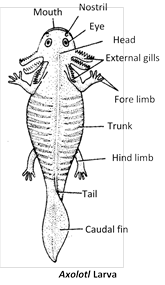
(2) Limbs 2 pairs, usually weak, almost equal.
(3) Skin devoid of scales and tympanum.
(4) Gills permanent or lost in adult.
(5) Males without copulatory organs.
(6) Larvae aquatic, adult-like, with teeth.
(7) It mainly includes Newts and Salamanders.
Examples : Cryptobranchus, Megalobatrachus, Ambystoma, Salamandra, Desmognathus, Amphiuma, Plethodon. Siren, Pseudobranchus, Triturus, Necturus.
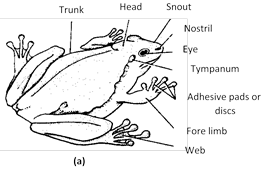
Order 3. Salientia or Anura : (L., saliens = leaping ) or (Gk., an = without ; nura = tail)
(1) Specialized amphibia without tail in adults.
(2) Hind limbs usually adapted for leaping and swimming.
(3) Adults without gills or gill openings.
(4) Eyelids well-formed. Tympanum present.
(5) Skin loosely-fitting, scale less; mandible toothless.
(6) Pectoral girdle bony. Ribs absent or reduced. Vertebral column very small of 5–9 pre sacral vertebrae and a slender urostyle.
(7) Fertilization always external.
(8) Fully metamorphosed without neotenic forms.
(9) It mainly includes frogs and toads.
Examples : Alytes, Bombinator, Discoglossus, Pipa, Xenopus, Pelobates, Scaphiopus, Bufo, Rhinoderma, Dendrobates, Hyla, Gastrotheca, Rana, Polypedates or Rhacophorus.
Common Names
|
Uraeotyphlus |
– |
Blindworm |
|
Ichthyophis |
– |
Caecilian |
|
Ambystoma |
– |
Tiger salamander |
|
Amphiuma |
– |
Congo eel |
|
Cryptobranchus |
– |
Hellbender |
|
Necturus |
– |
Mud puppy |
|
Proteus |
– |
Cave salamander |
|
Siren |
– |
Mud eel |
|
Triton |
– |
Newt |
|
Salamandra |
– |
Salamander |
|
Rana tigrina |
– |
Indian bull frog |
|
Alytes |
– |
Midwife toad |
|
Bufo melanostictus |
– |
Indian toad |
|
Pipa |
– |
Surinam toad |
|
Hyla |
– |
Tree frog |
|
Rhacophorus |
– |
Flying frog |
|
Bombinator |
– |
Fire bellied toad |
|
Xenopus laevis |
– |
African clawed toad |
|
Ascaphus |
– |
Bell toad |
|
Astylosternus |
– |
Hairy frog |
|
Nototrema (Gastrotheca) |
– |
Marsupial frog |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
