Liliaceae
Category : 11th Class
Systematic position
Division : Angiospermae
Class : Monocotyledonae
Series : Coronarieae
Order : Liliales
Family : Liliaceae
Habit : Usually perennial herbs growing by means of rhizomes (e.g., Aloe, Polygonatum), bulbs (e.g., Lilium, Allium) and corms (e.g., Colchicum). Some herbs are annual (e.g., Asphodelus). Shrubs occur in Aloe, Agave, Yucca (Dagger plants, Adam’s Needle), Dracaena (Dragon plant), and Ruscus (Butcher’s Broom). They mostly grow in arid areas and are hence xerophytic (e.g., Aloe, Yucca). Xanthorrhoea of Australia is tree-like. Climbers are seen in Smilax, Gloriosa and species of Asparagus.
Root : Adventitious, fibrous or tuberous (e.g., Asparagus).
Stem : Erect or climbing as Smilex, branched or unbranched, herbaceous, phylloclade as Ruscus. Cladode as Asparagus, Bulb as Allium cepa.
Leaves : Radical or cauline and ramal show various types of phyllotaxy (alternate, opposite or whorled), exstipulate, stipulate in Smilax where the stipules are prolonged into tendrils, sessile or petiolate with sheathing leaf bases, venation parallel but reticulate in Smilax, leaves may be scaly, leathery, fleshy or modified into spines (e.g., Asparagus), leaf apex is tendrillar in Gloriosa. The leaves of Phormium tenax (New Zealand Hemp) are 3 metres long and 10 cm broad.
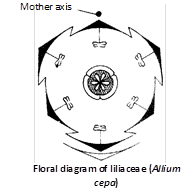
Inflorescence : Recemose, sometimes solitary (e.g., Tulipa, Gloriosa) or umbellate condensed cymes (umbel cyme), e.g., Onion. In several cases the inflorescence possesses a leafless peduncle called scape.
Flower : Bracteate or ebracteate, pedicellate, regular, actinomorphic, zygomorphic in a few cases (e.g., Gilliesia), complete or incomplete, perfect, unisexual in Smilax and Ruscus, hypogynous, generally pentacyclic, trimerous (rarely bimerous or tetramerous). Accessory floral organs undifferentiated and collectively called perianth.
Perianth : Tepals 6, in two whorls of 3 each, free or fused, sepaloid or petaloid, scarious or membranous, aestivation valvate or imbricate, distinguished into calyx and corolla in Trillium.
Androecium : Stamens 6 (3 in Ruscus, \[912\] in Tofieldia), free (polyandrous) or monadelphous (e.g., Ruscus), arranged in two whorls, antiphyllous (antitepalous), may be epiphyllous (or epitepalous), anthers fixed variously (basifixed, dorsifixed, versatile), dehiscence longitudinal or by pores.
Gynoecium : Tricarpellary, syncarpous, ovary superior, trilocular with 2-many ovules in each locules, placentation axile, rarely parietal, styles united or separate, stigma free or fused, trilobed.
Fruit : A capsule (e.g., Asphodelus, Gloriosa) or berry (e.g., Asparagus).
Seed : Endospermic and monocotyledonous.
Floral formula :
![]()
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
