Category : Teaching
Travel
Transportation is the movement from one location from another; this movement can be of goods, chemicals, medicines, animals and people for various reasons like travelling, economic activity and mobility. Economic growth of any nation has always dependent on better and rational transport system. Various transports mean consume major fossil fuels and create major air pollution. Air quality, global warming, ozone depletion, smog and acid rains are major issues that are caused increasing oxides of carbon and nitrogen. Transport is the fastest growing emission sector of these pollutants.
Travel or journey can be defined as movement of individual or group due to any specific purpose from one place to another. Term travel is used for movement of human being while term transport is used for movement of goods from one place to another.
People travel within the country as well as to other country. There are many reasons to travel, some of reasons are following
· Employment
· Educational purposes
· To avoid disaster
· Trade and business
· Pilgrimage
· Holiday
· Expedition
· Adventure etc.
India is vast and diverse country. Diversity of India can be defined in food habits, dressing, language, geography, agriculture, vegetation etc. Different kinds of geographic feature are found in India like hot deserts, cold deserts, mountains, plains, plateaus evergreen forests. etc. India is surrounded by neighbours like China, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, Sri
Lanka, Pakistan and Afghanistan.
· At present, India has 29 States and 7 Union Territories, Jammu and Kashmir is the
· Northernmost state of India, Tamil Nadu is Southernmost state while Arunachal Pradesh is
· Easternmost and Gujarat is the Westernmost state of India.
· New Delhi is the capital city and Mumbai is called financial capital of India.
8.1 Means of Transport
The means of transport can be classified into four types. These are given below
8.1.1 Roadways
Road transport is the popular and suitable means of transport for short distance. Roads can be made up of cement, concrete, coaltar etc. This type of road is called pucca road while road made up of soil is called kutcha road. Road transport has unique specificity that it can go to doorstep of the house and it can be constructed in the difficult geographical terrain.
Road transport is best mode of transport-to-transport easily perishable food products like vegetables, fruits, milk etc.
Roads have been categorised into six categories in India
1. Golden Quadrilateral The government has launched a major road development project linking Delhi - Kolkata, Chennai - Mumbai by six lane super highways. The North-South corridors linking Srinagar (Jammu and Kashmir) and
Kanyakumari (Tamil Nadu) and East-West corridor connecting Silcher (Assam) and Porbander (Gujarat) are part of this project. The major objective of these super highways is to reduce the time and distance between the mega cities of India. These highway projects are being implemented by National Highway Authority of
India (NHAI).
2. National Highways These are the primary road systems and Central Public Works Department (CPWD) is the authority for national highway maintenance.
3. State Highways State capital is linked by different district headquarters by state highways.
Construction and maintenance of state highways is under. State Public Works Department (PWD) in State and Union Territories.
4. District Road District headquarter is connected with other places of the district by district roads.
These roads are maintained by Zila Parishad.
5. Other Roads Rural roads, which link rural areas and villages with towns are classified under this category. These roads received special impetus under the Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana. Under this scheme, special provisions are made so that every village in the country is linked to a major town in the country by an all season
motorable road.
6. Border Roads Roads in the border areas of the country is construct and maintain by Border
Road organisation (a Government of India undertaking). This organisation was established in 1960 for the development of the roads of strategic importance in the Northern and North-Eastern border areas.
Facts Related to Road Transport
· India is connected to Bangladesh, Myanmar, Nepal, Bhutan, Pakistan and China by road.
· National Highway No 7 is longest highway in India and it connects Varanasi and Kanyakumari.
· NH-47 A is the smallest highway.
· Longest bridge on road in India is ?Mahatma Gandhi Setu?. It is in Patna.
· Leh-Manali highway is the highest highway in the world.
· Sher Shah Suri road also known as Grand Trunk Road connects Amritsar and Kolkata. NH-1, NH-2 and NPI-91 are parts of this highway. It is between
Kolkata and Amritsar.
8.1.2 Railways
Railways conduct multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances.
Indian Railways have been a great integrating force for more than 150 years. Railways had started in 1853 between Mumbai and Thane, covered a distance of 34km.
Rail Gauge and Length of Routes in India
|
Gauge (in m) |
Route |
Running Track (km) |
|
Broad gauge (1.676 m) |
46807 |
66754 |
|
Meter gauge (1) |
13209 |
13976 |
|
Narrow gauge 0.762 & 0.610 |
3124 |
3129 |
Narrow gauge mainly limited in hilly areas.
Railway Zones
Indian railways is divided in 17 zones and 70 divisions. These are given below in following table
|
Zone |
Headquarter |
|
Central Railway (CR) |
Mumbai |
|
Eastern Railway (ER) |
Kolkata |
|
Northern Railway (NR) |
New Delhi (Biggest zone) |
|
North-Eastern Railways |
Gorakhpur |
|
North-East Frontier Railway (NEFR) |
Guwahati |
|
Southern Railway (SR) |
Chennai |
|
South Central Railway (SCR) |
Secunderabad |
|
South-Eastern Railway (SER) |
Kolkata |
|
Western Railway (WR) |
Mumbai |
|
East Central Railway (ECR) |
Hajipur |
|
East Coastal Railway (ECR) |
Bhubaneswar |
|
North Central Railway (NCR) |
Allahabad |
|
North-Western Railway (NWR) |
Jaipur |
|
South-East Central Railway (SECR) |
Bilaspur |
|
South-Western Railway (WCR) |
Jabalpur |
|
Kolkata Metro |
Kolkata (29th December) |
Facts Related to Indian Railways
· India has the second largest railway network in
· Asia after China and 4th largest in the world.
· Fastest train in India is Gatiman Express which runs at maximum speed of 160 km runs between New Delhi and Agra.
· Longest rail route is between Dibrugarh (Assam) and Kanyakumari (Tamil Nadu). This route is abou1 4286 km long.
· World's longest platform is at Gorakhpur, its length about 1.3 km.
· Konkan railway is between Maharashtra and Karnataka and its length is about 760 km. Its unique feature is that it passes through Western Gnat's mountains by means of tunnels and bridges.
· Jammu-Baramula rail route is located in Jammu and Kashmir. It runs about 342 km and stations like Udhampur, Srinagar is located on it.
Mountain Railway of India
These trains run in the mountainous region of India.
1. Darjeeling Himalayan railway
2. Nilgiri Mountain railway
3. Kalka-Shimla railway
4. Kangra-Valley railway
Metro Railway
First metro rail started in Kolkata. Now, it is running in many cities of India like Delhi, Jaipur, Chennai, Mumbai and Bengaluru, in Delhi, Metro started in 2002. Monorail operates in Mumbai only.
Vivek express is a chain of express trains. These were announced in Railway Budget 2011-2012 on 150th Birth Anniversary of Swami Vivekanand. One of the Vivek Express trains, run on longest train route (Dibrugarh to Kanyakumari).
Ticket and Time-Table Ticket
For travelling by any means of public transport i.e. railways, roadways, airways and waterways, one needs to take a ticket. Tickets are of two types (i) Reserved and (ii) Unreserved
Reserved Ticket
This variety of ticket contains all relevant details about number of passenger, passengers seat or berth, age, sex, name may or may not be given on ticket, his boarding and destination point. It also carries detail about medium of transport being used i.e. bus number, train number, flight number etc, arrival and departure time.
Date of journey, date of reservation or booking, class of seat or coach in which reservation is i.e. Sleeper, 3AC, 2AC, first class in railways, economy or business class in plane etc. Total fare of journey is also denoted on the ticket.
Unreserved Ticket
This kind of ticket does not have full detail about journey. Very minute details like boarding and destination point, date of journey, fare of journey etc are written on it only.
Time-Table
It is a kind of booklet or guide which contains the information regarding travel between different places. Time-tables contain details about all available routes between different places, distances between different places and the places or station which will come during the journey while travelling from one place to another and at what time these stations will come, how much will be the stoppage time and what the departure time is from those stations etc.
Time, Distance and Speed
· Time Time can be defined as a period in which any vehicle or means of transport cover any distance.
· Distance It is a length covered by any means of transportation in a given time.
· Speed The rate at which something moves or travel.
· The relationship between speed, distance and time is expressed as
\[Speed=\frac{\text{Distance}}{Time}\]
\[Time=\frac{\text{Distance}}{Speed}\]
\[Distance=Speed\times Time\]
8.1.3 Water Transport
It is the cheapest means of transport and it is most convenient way of transport of goods in the international market.
Water transport is of two types
Inland Waterways
India has an extensive network of inland waterways in the form of rivers, canals, backwaters and creeks.
India has its unique advantage as 14 states are bestowed with 7500 km of coastline with 14500 km of potentially navigable waterway inland water transport is cheapest and environment friendly mode of transport.
Inland waterways authority of India is working on new projects for waterways and better water transportation in India.
Six major inland waterways are as follow
1. National Waterway 1 It is longest waterways in
India, starts from Allahabad to Haldia with distance 1620 km. This waterway run through,
Ganga, Bhagirathi and Hoogly river system.
2. National Waterway 2 This waterway is from Sadiya to Dhubri on river Brahmaputra, in Asom state. It is the IIIrd longest waterway (891 km).
3. National Waterway 3 (West Coastal Canal) It is located in Kerala state and run from Kollom to
Kottapuram. It has all time navigation facility.
4. National Waterway 4 It connects Kakinada to Puducherry through canals, tanks and river.
Godavari along with Krishana river lind longest waterway with 1095 km length.
5. National Waterway 5 This waterway connects
Orissa to West Bengal. Brahmani river, East coast canal, Matai river and Mahanadi river delta all are the parts of NW-5.
6. National Waterway 6 It is proposed in Asom and will connect Lakhipur to Bhanga in river Barak.
International Waterway
India has around 7517 km long coastline in India 95% according weight and 70% according value international trade done by oceanic way.
International sea water route of India is connected to different countries. These are
From Mumbai Port
Pakistan, Arab countries, Europe, Africa.
From Chennai Port
Sri Lanka, Australia.
From Kolkata Port
Myanmar, Malaya, Indonesia, Australia.
Important Ports of India
These ports are connected with port of other countries. Important ports of India are as follow
· Kandia Port - Gujarat
· Nhava Sheva - Maharashtra
· Mumbai Port - Maharashtra (largest port of India)
· Marmagao Port - Goa
· Panambur Port - Karnataka
· Cochin Port - Kerala
· Port Blair - Andaman
· Tuticorin - Tamil Nadu
· Chennai Port-Tamil Nadu (IInd longest port and oldest port)
· Indira Gandhi lake is largest lake in India.
· Nehru Trophy Boat Race is a popular Vallam Kali held in 'Punnamada Lake' of Kerala. The-most popular event of the race is the competition of Churidar Vallams (snake boats),
8.1.4 Air Transport
It is the fastest and expensive mode of transport.
Whole world is nearly connected by means of air transport. There are 12 international airports in India and many domestic airports. Through air transport, place with highly difficult terrain can be connected easily.
From 1911, air transport had been started for postal services from Allahabad to Naini. In 1953, air transport was nationalised.
Few international airports of India are following
|
International Airporte |
City |
|
Rajiv Gandhi International Airport |
Hyderabad |
|
Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport |
Mumbai |
|
Kempegowda International Airport |
Bengaluru |
|
Netaji Subhash Charidra Bose International Airport |
Kolkata |
|
Thiruvananthapuram International Airport |
Thiruvananthapuram |
|
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport |
Ahmedabad |
|
Indira Gandhi International Airport |
Delhi |
|
Meenambakkam International Airport |
Chennai |
Pawanhans
Pawanhans helicopters Ltd provides helicopter services to oil and Natural Gas Commission in its off-shore operations to inaccessible areas and difficult lands like North-Eastern states, Himachal
Pradesh, Uttaranchal and interior part of Jammu and Kashmir.
8.2 Different Kinds of Travel
Other than the usual travel which people undertake for employment, education, visiting relative etc.
Travel is also undertaken for exploration, discovery, tourism and expedition. Such travel include space travel, mountain climbing, eco-tourism, visiting historical places etc.
8.2.1 Space Travel
· With development in technology and advancement in science. It is possible to go into space. In space, gravity is absent and due to absence of gravity things keeps on floating in the space.
· The sun, the moon, stars, planets, satellites, asteoroid, meteoroid etc are all found in the space. Surface of the moon is rough with deep craters, high mountains and there is no water on the moon.
· Shooting star is meteoroid, it is made up of small rocky or metallic body which catches fire due to atmospheric friction as it enters Earth atmosphere.
· In space, water does not stay at one place. It float around as blobs. To wash face one needs to catch these blobs and wet paper with them. Papers are stuck to the wall of spaceship otherwise it will also float. There is no need to comb, as hair kept standing all the time.
· On the Earth, things fall and rest at one place due to gravity.
· Neil Armstrong was the first man to walk on the moon in 1969. Sunita William, an American astronaut, holds the record for maximum time spent and number of space walk by woman.
· Rakesh Sharma was the Indian who stepped in space.
· 2nd April, 1984 was the historical day when he (Rakesh Sharma) became the first Indian to travel in space, he made his flight abroad the Soyuz t-11.
· Kalpana Chawla was an Indo-American astronaut and first Indian woman to visit space, she died in space shuttle disaster in 2003.
8.2.2 Climbing on Mountain
· Climbing on the mountain is a tough task. For this, body needs to physically and mentally fit as one will have to bear physical pain and mental stress while climbing mountain.
· As one climbs mountain with increases in height level of oxygen decreases in atmosphere so there can be breathing problem. So, mountaineer carry oxygen cylinder along with them.
· For trekking one need to be trained and physically fit. A group leader for mountain trekking holds the responsibility to keep the group ahead and keep himself at the last.
· Leader should help other member of group in climbing and find a suitable place to rest in between during the trekking. Leader should help other member in carrying their bags who are not well and provide medicine to unwell member.
· Snow storm posses great danger to all mountaineer as it can cause physical injury to them, it can bury the mountaineer in the ice and can also cause fever and cold.
· Mount Everest is the highest mountain peak on the Earth. Its peak is at 8848 metre above the sea level. It belongs to the Nepal Himalaya. In Nepal, it is known as Sagarmatha and in Tibet is called
Chomolungma Himalaya.
· Bachhendri Pal became the first Indian woman and fifth woman in the world to reach peak of
Mount Everest,
8.2.3 Eco-Tourism
It is a tourism which is directed towards natural environment and helps in protecting and conserving nature and wildlife.
Eco-tourism plays an essential role in maximizing environment and social benefit of tourism. India have many places to promote eco-tourism e.g.
North-Eastern India, Jammu and Kashmir,
Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala and Goa.
A Visit to Abu Dhabi
Abu Dhabi is located in the desert, here water is very precious. There is no rain, no lakes, no rivers, no ponds and not even a ground water but there is lot of oils below the sands. Only date palm tree grows in the desert. In Abu Dhabi, there is tall building with big windows but windows cannot be open because of heat outside. Weather is so hot than people wear loose cotton clothes and keep themselves fully covered. In Abu Dhabi, Dirham is used as currency and local launguage on which most of the people speak is Arabic.
Visit to Golconda Fort and Museum
Golconda fort is huge fort made up of thick walls and at some places wall comes out in a round shape called bastion. Bastion were there to ensure security effort.
These fort were built in 1200 from then different ruler lived there, from 1518 to 1687 Qutubshahi Sultan ruled here. Map of the fort showed many garden fields and factories. In fort not only king but many other people like farmers and workers also lived. Fort has 2 storey building, it had big haills and rooms with beautiful carving on the wall, it had fountain on the roof and big water tank was also there. Fort had many cannons, which were used in the war, there were also big guns and these guns were made up of bronze. At
Fateh Darwaza in the fort sound echoed and if any one speaks at this place it can be heard at kings palace. Mehrabs (arch) were found in the fort. Fort had special arrangement for water, bullock were used to fetch the water. Clay pipes were still found in wall of the fort. Through these pipes water were carried to different place. In museum, many old items are kept.
When historical places are dug many things are found e.g. pot, jewellery, sword, small plate made up of bronze, (it is alloy of copper and tin), ceramic material etc. It is through these things we come to know, how people of those time lived and what they used and made. In museum many ancient things, crafts, paintings, objects etc are also found.
8.3 Fuels and Energy
Source
Work can be done by energy. The sun, wind, water, coal, petroleum etc are all natural source of energy.
Some of these are non-renewable like coal and petroleum and solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy are renewable source of energy. Main sources of energy are listed below
Coal
Coal is a non-renewable energy source because it takes millions of years to forms. Carbon is its main constituent.
Coal is mainly used for formation of electricity, coal and coaltar. West Bengal and Jharkhand are main coal producing - State in India.
Petroleum
Petroleum is also a fossil fuel. That was formed from the remain of ancient marine organisms and
Vegetations. It is refined and separated by distillation process into gasoline (petrol), lubricants, deisel carosine oil and gas etc. Mainly petroleum is used in automobile, paints and dry cleaning etc.
Natural Gas
Over millions of years, layer after layer or sediment of animals, plants and bacteria were formed. The amount of pressure and degree of heat along with the type of biomass determine the final product as oil or natural gas. Two types of natural gas are given below"
1. Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG) The components of LPG are gases at normal temperature and pressure. Its main constituent is butane. Because it is a colourless and odourless gas ethyle mercaptan is mixed to know about its leakage.
2. Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) It is formed by using high pressure. Its main constituent is methane. CNG is used in place of gasoline.
Hydroelectricity
It is obtained from water flow or water falling from a height. Hydro power converts power of the falling water to electricity power which can be transmitted to long distance through wire and cables.
Environmental imbalance and rehabilitation is the major issues of this type of electricity.
Solar Energy
It is convert into electricity through solar cells.
Silicon and galium is used in solar cells.
Wind Energy
Wind turbins convert the kinetic energy in the wind into mechanical power. 20 km/hour should be the speed of wind for making wind energy.
Geothermal Energy
Resources of geothermal energy is hot water found a few miles beneath the Earth surface and down deeper to the extremely high temperature of molten rock (magma). In India, mainly Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh and Puga valley in Kashmir produce geothermal energy.
Biogas
It is formed by break down of organic matter in die absence of oxygen. Raw material for its production are agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, sewage etc. Main component of biogas are methane
(55-70%) \[C{{O}_{2}}\] (30-45%), \[{{H}_{2}}S\] and ammonia.
Nuclear Energy
It is formed by the fission of uranium and thorium in nuclear reactors. It is a non-conventional energy.
Biodiesel
The process used to convert these oils to biodiesel is called ?transesterification?. Karkas, pongomia, jatrofa is used in production of biodiesel.
8.4. Air Pollution
A physical, biological or chemical alteration to the air in the atmosphere is termed as pollution.
Factors Responsible for Air Pollution
Factors which are responsible or air pollution are given below
Effects of Air Pollution
Air pollution effects on environment and on human in different ways. These are
· Respiratory and skin problems
· Global warming
· Acid rain
· Depletion of ozone layer
Solutions
To overcome the problem of air pollution, we must follow following steps
Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM)
These are microscopic solid or liquid matter suspended in the atmosphere. Particulate matter includes dust, smoke, soot, pollen and soil particles.
Smog
It is a type of air pollution. Smog is the mixture of smoke and fog. Smog is composed by nitrogen oxides, sulphur oxide, ozone, smoke.
Ozone Layer
It is present in stratosphere at an altitude of about
10 km. Ozone concentration is high here. Ozone layer absorb harmful ultra violet rays emitted by
Sun. Dobson unit is a measurement of ozone in the atmosphere above a point on the Earth's surface.
Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
The greenhouse effect is naturally occurring phenomenon that is responsible for heating of
Earth's surface and atmosphere. \[C{{O}_{3}}\] and Methane gases are greenhouse gases increase in the level of greenhouse gases has led to considerable heating of Earth leading to global warming.
Famous Travellers
From the ancient time, many travellers are coming to India and they have provided very useful information about India of that period.
Megasthenes He came in the court of
Chandragupta Maurya, He has written a book named Indica. He came from Greece.
Fahien He was a Chinese traveller, he came to India during the period of Chandragupta Vikramaditya.
His account tells about the condition of that period.
Hiuen Tsang He was also Chinese traveller. He came to India during reign of Harsha. He studied in Nalanda University. He was Buddhist monk also.
Al-Biruni He came with Mahmud of Ghazni. He belonged to Uzbekistan. He has written Tahqiq-i-Hind and Kitab-ul-Hind. He gave descriptive account about water bodies, river, ponds etc.
Ibn-Battuta He came to India during the reign of Tughlaq. He originally belonged to Morroco. He also wrote a book Rohela in which he gave account about India of that period.
Vasco-Da-Gama A Portuguese traveller came to
India in 1498 via the sea-route and he landed at
Calicut.
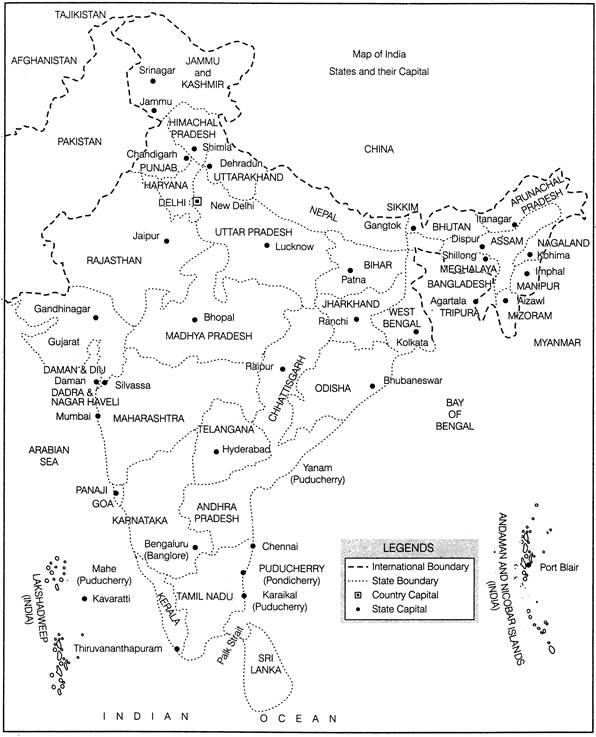
Different states, their capital, city and neighbouring states and directions of travel while travelling from one place to another can be known from the map.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
