Category : 8th Class
Reproduction and Adolescence
Reproduction
Reproduction is a biological process by which new individual organism-off springs-are produced from their parents. Reproduction is one of the essential functions of plants, animals and other organisms for the preservation of the species. In almost all animals, reproduction occurs during or after the period of maximum growth.
Types of Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
It is a type of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single organism and it does not involve the fusion of gametes.
Types of Asexual Reproduction
Binary fission - in this type of reproduction the fully grown parent cell splits into two halves, producing two new cells. For example, amoeba and paramecium.
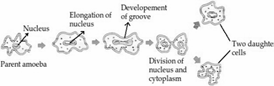
Binary fission in Amoeba
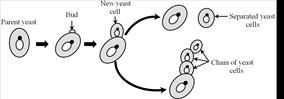
Budding In Yeast
Vegetative Propagation - is found in plants where new independent individuals are formed without the production of seeds and spores. For example, propagation through leaves in Kalanchoe, Bryophyllum.
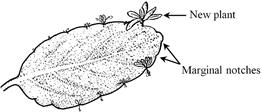
Vegetative propagation by leaves in Bryophyllum
Spore Formation - is found in nonflowering plants such as fungi and bacteria. In this method, the plant produces hundreds of tiny spores which can grow into new plants.
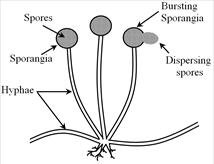
Spore formation in Rhizopus
Fragmentation - in this method a new organisms grows from a fragment of the parent. Each fragment develops into a mature, fully grown individual. For example, lichens, liverworts.
Fragmentation in Spirogyra
Sexual Reproduction
It is a method of reproduction of producing a new individual from two parents by combining their genetic information. For example, human beings, dog, cat, etc.
Fertilisation
The process of formation of zygote by the fusion of male gamete and female gamete is known as fertilisation. There are two types of fertilization: internal and external fertilisation.
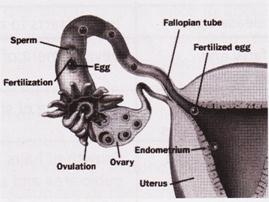
Fertilisation in humans to form a zygote (fertilised egg)
Gametes
Gametes are the cells involved in sexual reproduction. In humans male reproductive organ is testes and female reproductive organ is ovaries. Male gamete in animals is called sperm and the female gamete in animals is called egg.
Zygote
The new cell which is formed by the fusion of male and female gamete is called zygote.
Adolescence and Puberty
Adolescence, the period of transition between childhood to adulthood, begins around the age of 11 years and lasts up to 18 or 19 years of age. It is considered to start with the onset of puberty. Puberty is a period of transformation from a stage of reproductive immaturity to a stage of full reproductive competence. Adolescence is the period in the life scan of a person when he or she attains the ability of reproduction.
Changes at Puberty
The main physical changes which take place during the period of puberty are as follows:
|
Girls |
Boys |
|
Increase in height |
Increase in height |
|
Ovaries start to release eggs |
Testes starts to male sperms |
|
Development of fatty and subcutaneous tissues |
Development of muscles
|
|
Broadening of hips. Extra fat is deposited on hips and thighs |
Broadening of shoulders and chest
|
|
Growth of hairs in armpits and pubic area |
Growth of hairs in the armpits, public area and appearance of facial hair |
|
Voice becomes shrill |
Voice deepens |
|
Breasts develop and get enlarged |
Increase in the size penis
|
|
Onset of menarche |
Nocturnal emissions take place |
Hormones and their Functions
|
Glands |
Hormone secreted |
Function |
|
Pituitary gland |
several hormones including growth
|
1.Stimulates thyroid gland for thyroxin production 2. controls normal growth 3. controls the functioning of other |
|
Thyroid gland |
Thyroxin |
Controls the rate of body?s metabolism |
|
Adrenal gland |
Adrenalin |
1.prepare our body to function at maximum efficiency during emergency situations 2.Maintains correct salt balance in blood |
|
Pancreas |
Insulin |
Sugar metabolism |
Reproductive Phase in Humans
An adolescent become capable of reproduction when testis and ovaries start to produce gametes in males and females respectively. The production of gametes starts earlier in females than in males. In females, this phase begins at the age of 10 to 12 years while in males, it begins at 12 to 14 years of age. However, the production of gametes lasts for a much longer time in males than the females. In females, the reproductive phase or production of gametes generally lasts upto the age of 45 to 50 years. This period from the onset of puberty to the age of 45-50 years when production of gametes stops, is marked by a specific event repeated almost every month. During this period, one ovum matures and is released by one of the ovaries once in about 28-30 days and the inner lining of the uterus becomes thick and spongy so as to receive the egg. In case it is fertilized, it starts developing to form an embryo and results in pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, the egg released by the lining of the uterus along with its blood vessels is shed off. As a result, bleeding takes place in women. This loss of blood is called menstruation. Menstruation occurs once in about 28-30 days. The first menstrual flow begins at puberty and is called menarche. Around the age of 45 to 50 years, the menstrual cycle stops. The permanent stoppage of menstruation is called menopause.
Reproductive Health
Reproductive health is defined as a state of physical, mental and social well-being in all matters relating to the reproductive system, at all stages of life. Good reproductive health is more essential during the period of adolescence because in this period body is growing rapidly and other important changes takes place.
Conditions to maintain good reproductive health during adolescence are:
(i) Eat balanced diet
(ii) Take adequate physical exercise, rest and sleep
(iii) Maintain personal hygiene
(iv) Stay away from alcohol
(v) Say no to drugs
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
