Category : 4th Class
Activity
This activity helps students identify noun and encourages interest in current affairs. The activity can be done individually or in small groups. Each student or groups. Each student or group is given an age-appropriate newspaper or magazine article. The student divides a sheet of paper into three sections, labeling the sections singular, plural and possessive. The student lists the nouns in the article under the appropriate section of the chart.
LOWING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to:-
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
Definition: A noun is the name of a person, place, or thing; as Saurav, Kolkata, dog/ cottage, gold, platinum, swarm, flight, honesty, patience.etc.
KINDS OF NOUN
There are five different kinds of noun
(a) Proper Noun: It is the name of a particular person or place and is always written with a capital letter. Eg, Ashoka was a great king. The Ganga is a sacred river. The Howrah bridge is situated in Kolkata.
(b) Common Noun: It is a name which is common to any and every person or thing of the same kind. Eg, the girl is writing a letter. Lion is the king of jungle. We should always respect our teachers.
(c) Collective Noun: It denotes a number of persons or things grouped together as one complete whole. Eg, Fleet of ships are standing in the harbour. Keep the bunch of keys safely with you. The Indian cricket team won the World cup in 2011.
(d) Material Noun: It denotes the matter or substance of which things are made. Eg, Gold is used to make jewellery. Mason works with bricks and cement. Camels can run easily on sand.
(e) Abstract Noun: It is the name of some quality, state or action considered to be apart from the thing to which it belongs. Eg, Honesty, bravery, motherhood, patriotism, infancy, etc.
(A) Proper Noun:
The Taj Mahal is situated in Agra
(B) Common Noun:
An elephant can carry heavy logs of wood in its trunk.
(C) Collective Noun:

A herd of cattle is grazing in the field.
(D) Material Noun:
Wood is used to make furniture, doors and windows.
(E) Abstract Noun:

Friendship is our greatest strength.
Misconcept / Concept
Misconcept: Possessive noun demonstrate ownership or a relationship over Something Possessive noun will have an apostrophe which indicates the ownership. It is common for individuals to confuse possessive nouns with plural nouns.
Concept: The Possessive answers the question_ _ _ _ _ whose?. The possessive case of a Singular Noun is formed by adding ('s); as The girl's pen, the horse's tail, the king's palace. The Possessive case of a plural Noun ending in 's' is formed by adding the apostrophe (') only; as Boys' books, birds' nests, horses' tails. Once you have learned about possessive nouns and completed a series of worksheets it is beneficial to take a series of quizzes in order to test your understanding and usage of possessive nouns.
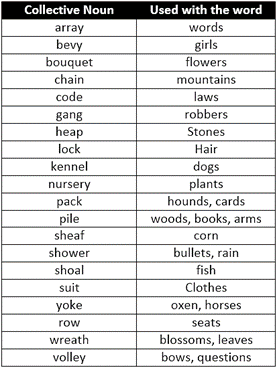
A. WORDS SHOWING COLLECTION
B. FORMATION OF ABSTRACT NOUNS
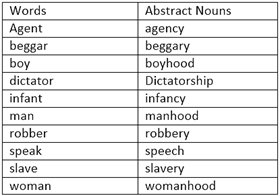
C. FORMATION OF ABSTRACT NOUNS

Gender Formation: There are four types of gender.
(a) Masculine- Male animal or human.
Example: Man, deer
(b) Feminine- Female animal or human.
Example: Woman, doe
(c) Common- When we are not sure if the person or animal is male or female.
Example: Parent, adult, child
(d) Neuter- For non- living things.
Example: Book, table
Plural Formation: There are various rules to form plurals.
(a) Add 's' to the singular noun.
Example: Girl-girls, boy- boys
(b) Add 'es? to the singular noun which ends with 'ch', 'sh' or 'x'.
Example: Branch- branches, brush- brushes, tax-taxes.
(c) Words which have y in the end and there is a consonant before y, y changes into I and then we must add 'es'. Baby- babies, lady- ladies.
(d) We add 'es' to the words ending with o.
Example: Mango-mangoes. But there are exceptions to this rule. Example: Photo-photos, Cargo-cargos.
(e) Words ending with f/fe will change into 'v' and then 'es' is added.
Example: Thief-thieves, knife-knives. But there are exceptions to this rule. Example: Handkerchief-handkerchiefs, chief chiefs, safe-safes.
(f) In few words we add 'en'.
Example: Child- children, ox- oxen.
(g) Few words are alike in their singular and plural forms.
Example: Deer, sheep, salmon, aircraft, spacecraft, series, species.
(h) Words with numbers before them will be said in singular form but if there js no number written before them they may be said in plural form as well.
Example: 2 pair of socks, 10 thousand. If there is n number-pairs, thousands, dozens, hundreds.
(i) Collective noun is said in singular form only.
Example: Herd, army, bouquet etc.
(j) There are few objects which are said in plural even they are singular.
Example: Scissors, tongs, jeans, trousers, spectacles, etc.
(k) We do not make plural for abstract noun. Example: Honesty, kindness.
(l) For compound words, we add *s' to the main word.
Example: Mother-in-law changes to mothers in law, commander in chief changes to commanders-in chief.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
