Category : 4th Class
Measurement
Learning Objectives
In previous chapter, we have studied about shapes based on their properties. Perimeter and area are important concepts in our daily life as they widely applied by builders, painters, farmers, and gardeners. Perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a closed shape whereas the space inside the closed shape is its area. In this chapter, we will learn how to estimate and find the perimeter and area of geometrical shapes.
Example:
(a) \[\text{64 }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(b) \[\text{56 }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(c) \[\text{49 }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(d) \[\text{30 }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation: Here, length of the room = 8 m, and its breadth = 7 m
Therefore, the area of room = \[\text{length}\times \text{breadth}=(8\times 7)\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}=56\text{ }{{m}^{2}}\]
Hence, Amit needs to buy \[\text{56 }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\] carpet to cover his entire living room.
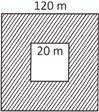
(a) \[14400\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(b) \[25600\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(c) \[10000\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(d) \[14000\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation: Area of swimming pool = \[\text{side}\times \text{side}=(20\times 20)\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}=400\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
Area of the garden including swimming pool = \[\text{side}\times \text{side}=(120\times 120)\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}=14400\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
Therefore, area of garden = area of garden including swimming pool \[-\] area of swimming pool
= \[\text{(14400}-400)\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}=14000\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
3. Perimeter of a square piece of gold is 22 millimetres. What is the length of each side of the piece of gold?
(a) 11 millimetres (b) 5.5 millimetres
(c) 5 millimetres (d) 4.5 millimetres
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation: Here, the perimeter of square piece of gold = 22 millimetres
Since, perimeter = \[4\times \]side of square
Therefore, each side of the square piece of gold \[=\frac{\text{Perimeter}}{4}=\frac{22}{4}\] millimetres = 5.5 millimetres
4. The figure given below is made up of identical squares. What is the perimeter of the figure?
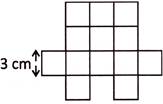
(a) 54 cm (b) 60 cm
(c) 66 cm (d) 72 cm
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation:
Length of each square = 3 cm
Number of outer sides of all squares = \[2+1+2+1+3+3+1+3+3+1=20\]
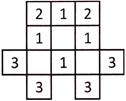
Hence, the required perimeter = (\[3\times 20\]) cm = 60 cm
Commonly Asked Question
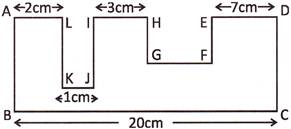
(a) 5 cm (b) 6 cm
(c) 7 cm (d) 8 cm
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation: Here,
BC = AL + KJ + IH + ED + GF = (2 + 1 + 3 + 7) cm + GF = 13 cm + GF = 20 cm
Therefore, GF = BC \[-\] (AL + KJ + IH + ED) = (\[20-13\]) cm = 7 cm
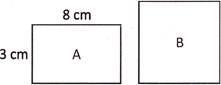
2. Perimeters of the given rectangle A and square B are same. Find the side of square B.
(a) 5.5 cm (b) 6.0 cm
(c) 6.5 cm (d) 5.0 cm
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation: Here, length of rectangle A = 8 cm, and its breadth = 3 cm
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle A = \[2\times (8+3)\] cm = (\[2\times 11\]) cm = 22 cm
So, we have the perimeter of square B = 22 cm
Since, perimeter of a square = \[4\times \text{side}\]
Hence, the side of square B = \[\frac{\text{Perimeter}}{4}=\frac{22}{4}\] cm = 5.5 cm
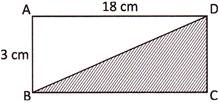
3. Area of triangle BCD is half of the area of rectangle ABCD. Find the area of triangle BCD.
(a) \[25\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(b) \[26\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(c) \[27\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(d) \[28\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation: Here, the length of rectangle ABCD = 18 cm and breadth = 3 cm
Therefore, the area of rectangle ABCD = \[\text{length}\times \text{breadth}=(18\times 3)\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}=54\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
Now, the area of triangle BCD = half of the area of rectangle ABCD
Hence, the required area = \[(54\div 2)\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}=27\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
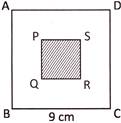
4. Area of inner square PQRS is one-third of the area of outer square ABCD. Find the area of inner square PQRS.
(a) \[27\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(b) \[\text{18 c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(c) \[\text{29 c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(d) \[\text{54 c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation: Here, one side of outer square ABCD = 9 cm
Therefore, the area of outer square ABCD = \[\text{side}\times \text{side}=(9\times 9)\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}=81\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
Now, the area of inner square PQRS is one-third of the area of outer square ABCD.
Hence, the required area = \[\frac{81}{3}\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}=27\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
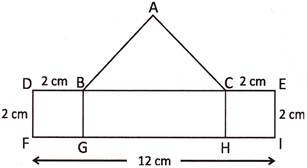
5. In the figure given below, the triangle ABC is an equilateral triangle. Find the perimeter of whole figure.
(a) 30 cm (b) 32 cm
(c) 34 cm (d) 36 cm
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation: Here, \[\text{GH}=\text{FI}-(\text{FG}+\text{HI})=\text{FI}-(\text{BD}+\text{CE})=\left[ \text{12}-(2+2) \right]\text{ cm}\]\[=(12-4)\text{ cm}=8\text{ cm}\]
Since, triangle ABC is an equilateral triangle.
Therefore, AB = AC = BC = GH = 8 cm
Hence, the required perimeter = AB + BD + DF + FI + EI + CE + AC
= (\[8+2+2+12+2+2+8\]) cm = 36 cm
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
