 Leaves
Photosynthesis
The process of making food by plants in the presence of sunlight, water, carbon dioxide and chlorophyll is called photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants take carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Food is prepared by plants in the form of glucose. Plants store extra food in fruits and seeds as starch. Trees store food in their trunks in the form of cellulose. Cactus do not have leaves. Photosynthesis occurs in their stems.
Leaves
Photosynthesis
The process of making food by plants in the presence of sunlight, water, carbon dioxide and chlorophyll is called photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants take carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Food is prepared by plants in the form of glucose. Plants store extra food in fruits and seeds as starch. Trees store food in their trunks in the form of cellulose. Cactus do not have leaves. Photosynthesis occurs in their stems.
 Cactus
Some plants are not green. For example, mushroom. Another plant like croton plant has red coloured leaves. The red colour of the leaves is due to the presence of anthocyanin. But they have chlorophyll also. Photosynthesis takes place in these plants also.
Cactus
Some plants are not green. For example, mushroom. Another plant like croton plant has red coloured leaves. The red colour of the leaves is due to the presence of anthocyanin. But they have chlorophyll also. Photosynthesis takes place in these plants also.
 Croton
Mushrooms do not have chlorophyll. They cannot make their food from photosynthesis. They get food from dead plants and animals.
Classification of Plants
Plants are of various types classified on the basis of where they grow.
Terrestrial Plants
Plant that grows on land are called terrestrial plants. They are further divided into various types such as:
Croton
Mushrooms do not have chlorophyll. They cannot make their food from photosynthesis. They get food from dead plants and animals.
Classification of Plants
Plants are of various types classified on the basis of where they grow.
Terrestrial Plants
Plant that grows on land are called terrestrial plants. They are further divided into various types such as:
 Mango tree
Plants in hilly areas
In hilly areas, plants can make food easily as there is sufficient sunlight and rainfall in these places. Coniferous tree grows on hills and mountains.
They have standing branches so that snow which falls on them more...
Mango tree
Plants in hilly areas
In hilly areas, plants can make food easily as there is sufficient sunlight and rainfall in these places. Coniferous tree grows on hills and mountains.
They have standing branches so that snow which falls on them more...  Insects
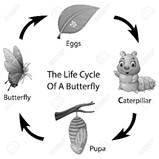
Insects also reproduce by laying eggs. Insects like butterfly and housefly have four stages in their life cycle i.e. egg, larva, pupa and adult. The egg is hatched into a larva.
The young one looks different from the adult. The larva of a butterfly is known as caterpillar and that of a housefly is called a maggot. The larva first grows rapidly by eating the leaves. Then after sometime, it stops eating and forms a covering around itself called as cocoon. This is called the pupa. The larva changes into an adult inside he pupa and comes out of it after sometime.
Insects
Insects also reproduce by laying eggs. Insects like butterfly and housefly have four stages in their life cycle i.e. egg, larva, pupa and adult. The egg is hatched into a larva.
The young one looks different from the adult. The larva of a butterfly is known as caterpillar and that of a housefly is called a maggot. The larva first grows rapidly by eating the leaves. Then after sometime, it stops eating and forms a covering around itself called as cocoon. This is called the pupa. The larva changes into an adult inside he pupa and comes out of it after sometime.
 Amphibians
Amphibians reproduce by laying eggs in water. The young frog which comes out of the egg is known as tadpole.
Fishes
Fishes also reproduce by laying thousands of eggs in water. But only few eggs grow into baby fishes.
Amphibians
Amphibians reproduce by laying eggs in water. The young frog which comes out of the egg is known as tadpole.
Fishes
Fishes also reproduce by laying thousands of eggs in water. But only few eggs grow into baby fishes.
 Reptiles
Reptiles lay eggs in the sand or rotting vegetation. They do not sit on the eggs to keep them warm. The sea makes them warm and the egg is hatched.
Animals Giving Birth to Young Ones
Mammals are the animals which give birth to young ones and produce milk to feed them.
They do not lay eggs. Dogs, monkeys, cats and human beings comes under the category of mammals. Bats are flying mammals. Whales and dolphins are also mammals living in water.
Habitat
The home or natural environment of a living thing is known as habitat. All living beings changes themselves to survive in the natural world, for example, birds and insects can fly. This is called adaptation.
Classification of Animals on the Basis of Their Habitat
Animals are classified on the basis of the place where they live.
Aquatic Animals
Animals which live in water are called aquatic animals. Fishes live in water. They have fins for swimming in water. They have gills for breathing. Aquatic animals like dolphins and whales do not have more...
Reptiles
Reptiles lay eggs in the sand or rotting vegetation. They do not sit on the eggs to keep them warm. The sea makes them warm and the egg is hatched.
Animals Giving Birth to Young Ones
Mammals are the animals which give birth to young ones and produce milk to feed them.
They do not lay eggs. Dogs, monkeys, cats and human beings comes under the category of mammals. Bats are flying mammals. Whales and dolphins are also mammals living in water.
Habitat
The home or natural environment of a living thing is known as habitat. All living beings changes themselves to survive in the natural world, for example, birds and insects can fly. This is called adaptation.
Classification of Animals on the Basis of Their Habitat
Animals are classified on the basis of the place where they live.
Aquatic Animals
Animals which live in water are called aquatic animals. Fishes live in water. They have fins for swimming in water. They have gills for breathing. Aquatic animals like dolphins and whales do not have more... 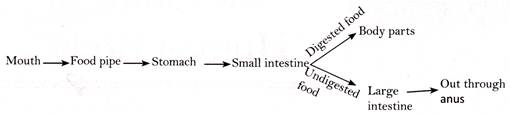
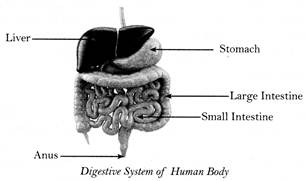 Digestive System of Human Body
Health Tips
Digestive System of Human Body
Health Tips
 The outer hard layer which covers the tooth is called enamel. Enamel is the hardest thing a human body. Dentine is below it. The core of the tooth is called pulp. Pulp is soft and has blood vessels and nerves in it. The nerves are connected to the gum through a hole in the root.
more...
The outer hard layer which covers the tooth is called enamel. Enamel is the hardest thing a human body. Dentine is below it. The core of the tooth is called pulp. Pulp is soft and has blood vessels and nerves in it. The nerves are connected to the gum through a hole in the root.
more... 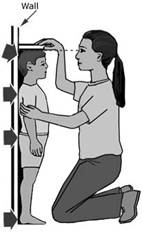 Measurement of Length
In early days, people used body parts to measure lengths.
Measurement of Length
In early days, people used body parts to measure lengths.
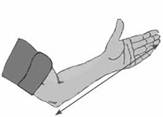
 Cubit Hand span
The metre is what we normally use for measuring lengths. Smaller lengths are measured centimetres. Metre is written as m and centimetre as cm.
Measurement of Mass
Mass tells us how heavy or light an object is. We us weighing scales to find the mass an object.
Just as we use metre for measuring length, we use kilogram for measuring mass. Smaller weights are measured in grams. Kilogram is written as kg and gram is written as g.
Measurement of Capacity
Capacity of a container is the amount of liquid it can hold. Litre is the commonly used unit for measuring capacity. Smaller units are measured in millilitres. Litre is written as / and millilitres as ml.
Some Other Units of Measurement
In everyday life, we also need to measure things that do not involve length, mass, and capacity. Time a temperature are two such examples. Time is measured in seconds. Measure of hotness or coldness of an object is called temperature. Temperature can be measured with the help of a thermometer.
Cubit Hand span
The metre is what we normally use for measuring lengths. Smaller lengths are measured centimetres. Metre is written as m and centimetre as cm.
Measurement of Mass
Mass tells us how heavy or light an object is. We us weighing scales to find the mass an object.
Just as we use metre for measuring length, we use kilogram for measuring mass. Smaller weights are measured in grams. Kilogram is written as kg and gram is written as g.
Measurement of Capacity
Capacity of a container is the amount of liquid it can hold. Litre is the commonly used unit for measuring capacity. Smaller units are measured in millilitres. Litre is written as / and millilitres as ml.
Some Other Units of Measurement
In everyday life, we also need to measure things that do not involve length, mass, and capacity. Time a temperature are two such examples. Time is measured in seconds. Measure of hotness or coldness of an object is called temperature. Temperature can be measured with the help of a thermometer.

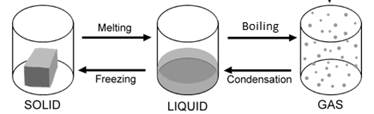 Changes Around Us
Matter is constantly changing around us. Changes are of two types — physical changes and chemical changes. In physical change, no new substance is formed. Breaking of glass, melting of ice into water are some examples of physical change. When ice melts the solid water turned to liquid water. It doesn't turn into food or cold drink or anything new. It remains water. Physical changes can be reversed.in a chemical change, new substance is formed. Changing of milk into curd is an example chemical change. Similarly burning of paper, making of vegetable dishes from raw vegetables, bursting of crackers are some other examples of chemical changes. Unlike physical changes, chemical changes cannot be reversed.
Rocks
Changes Around Us
Matter is constantly changing around us. Changes are of two types — physical changes and chemical changes. In physical change, no new substance is formed. Breaking of glass, melting of ice into water are some examples of physical change. When ice melts the solid water turned to liquid water. It doesn't turn into food or cold drink or anything new. It remains water. Physical changes can be reversed.in a chemical change, new substance is formed. Changing of milk into curd is an example chemical change. Similarly burning of paper, making of vegetable dishes from raw vegetables, bursting of crackers are some other examples of chemical changes. Unlike physical changes, chemical changes cannot be reversed.
Rocks
 A Man lifting a dumbbells
Elastic Force
It is the force exerted when an elastic material is stretched. For example, stretching of rubber band.
A Man lifting a dumbbells
Elastic Force
It is the force exerted when an elastic material is stretched. For example, stretching of rubber band.
 Stretching a rubber band
Frictional Force
It is the force exerted by two surfaces on each other in moves over the other, while they are in contact. For example, while walking on a road frictional force is acting between the road and the sole of our shoe.
Stretching a rubber band
Frictional Force
It is the force exerted by two surfaces on each other in moves over the other, while they are in contact. For example, while walking on a road frictional force is acting between the road and the sole of our shoe.
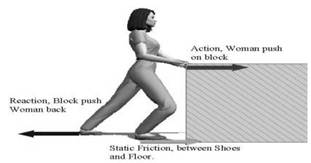 Friction, between shoes and Floor
Gravitational Force
The force exerted by the centre of the earth which pulls objects towards it. For example when a ball is thrown in the air, it comes back towards the earth due to gravitational force, an apple falling from a tree, etc.
Friction, between shoes and Floor
Gravitational Force
The force exerted by the centre of the earth which pulls objects towards it. For example when a ball is thrown in the air, it comes back towards the earth due to gravitational force, an apple falling from a tree, etc.
 Falling of an apple due to gravitational force
Electrostatic Force
When we rub a comb through dry hair, the comb gets charged and is able to attract tiny bits of paper. The force exerted by charged comb on the bits of paper is called electrostatic force.
Falling of an apple due to gravitational force
Electrostatic Force
When we rub a comb through dry hair, the comb gets charged and is able to attract tiny bits of paper. The force exerted by charged comb on the bits of paper is called electrostatic force.
 Charged hairs exert force on balloon
Work
Work refers to an activity that involves applying force on an object and movement the object in the direction of the force. For example, if a man lifts a bucket then some work is done. In this case, due to the force applied by the man, the movement bucket takes place in upward direction.
Simple Machines tools which make our work easy are called simple machines. For example, pulley, wheel and axle, lever, inclined plane, etc.
Charged hairs exert force on balloon
Work
Work refers to an activity that involves applying force on an object and movement the object in the direction of the force. For example, if a man lifts a bucket then some work is done. In this case, due to the force applied by the man, the movement bucket takes place in upward direction.
Simple Machines tools which make our work easy are called simple machines. For example, pulley, wheel and axle, lever, inclined plane, etc.
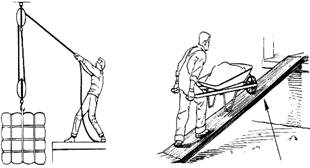 Pulley Inclined-plane
Energy
Energy is the capacity or ability more...
Pulley Inclined-plane
Energy
Energy is the capacity or ability more...  Pollution
Pollution is the undesirable change in the physical, chemical and biological constituents our surroundings. Pollution is of various types:
Air Pollution
Air pollution occurs when the air contains dust particles, gases, fumes in that amount which is harmful for us. The substances causing air pollution are called air pollutants. Industries and vehicles discharge harmful gases into the air making it dirty and unfit for breathing.
Pollution
Pollution is the undesirable change in the physical, chemical and biological constituents our surroundings. Pollution is of various types:
Air Pollution
Air pollution occurs when the air contains dust particles, gases, fumes in that amount which is harmful for us. The substances causing air pollution are called air pollutants. Industries and vehicles discharge harmful gases into the air making it dirty and unfit for breathing.
 Sun has ultraviolet rays which are absorbed by ozone layer present in the atmosphere. These rays can cause skin cancer. Due to air pollution ozone layer is getting depleted.
Effects of Air Pollution
Air pollution has various effects which are explained below.
Breathing Problem
When we inhale polluted air, it causes breathing problems. Bronchitis and asthma are diseases caused by air pollution.
Global Warming
Human inhales oxygen and gives out carbon dioxide, when amount of carbon dioxide increases in air, it causes global warming. Global warming is the heating up of atmosphere due to excessive amount of carbon dioxide in the air
Acid Rain
Sometimes harmful gases discharged by factories and vehicles mixes with water vapours in the clouds. When it rains, these harmful gases get mixed with water vapours and comes down as acid rain. It affects forests, soil and human health. Makes soil more acidic. It also damages buildings, monuments etc.
Water Pollution
When toxic substances enter lakes, rivers, oceans and other water bodies, it causes water pollution. There are many sources of water pollution. Sewage from cities is thrown it water resources without treatment. Polluted water causes diseases like jaundice, typhoid, diarrhoea etc.
Sun has ultraviolet rays which are absorbed by ozone layer present in the atmosphere. These rays can cause skin cancer. Due to air pollution ozone layer is getting depleted.
Effects of Air Pollution
Air pollution has various effects which are explained below.
Breathing Problem
When we inhale polluted air, it causes breathing problems. Bronchitis and asthma are diseases caused by air pollution.
Global Warming
Human inhales oxygen and gives out carbon dioxide, when amount of carbon dioxide increases in air, it causes global warming. Global warming is the heating up of atmosphere due to excessive amount of carbon dioxide in the air
Acid Rain
Sometimes harmful gases discharged by factories and vehicles mixes with water vapours in the clouds. When it rains, these harmful gases get mixed with water vapours and comes down as acid rain. It affects forests, soil and human health. Makes soil more acidic. It also damages buildings, monuments etc.
Water Pollution
When toxic substances enter lakes, rivers, oceans and other water bodies, it causes water pollution. There are many sources of water pollution. Sewage from cities is thrown it water resources without treatment. Polluted water causes diseases like jaundice, typhoid, diarrhoea etc.
 Factories discharges harmful chemicals directly into water which causes damage to aquatic plants and animals.
Soil Pollution
Land gets polluted when we dump garbage on it.
Factories discharges harmful chemicals directly into water which causes damage to aquatic plants and animals.
Soil Pollution
Land gets polluted when we dump garbage on it.
 Wastes are of two types:
Biodegradable: Things like fruits, vegetable peels, paper etc. get decayed by microorganisms and mixes with soil.
Non-biodegradable: Things like plastic, polythene which do not get decayed by microorganisms and remains as it is in the soil and pollute the soil.
Wastes are of two types:
Biodegradable: Things like fruits, vegetable peels, paper etc. get decayed by microorganisms and mixes with soil.
Non-biodegradable: Things like plastic, polythene which do not get decayed by microorganisms and remains as it is in the soil and pollute the soil.  The sun and the eight planets belong to a family called solar system. The eight planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. All of them revolve in fixed path called orbit. Planets rotate on their axis also. Most planets have their satellites which revolve around them. Satellite does not have its own light. Man has also made ne satellites for weather forecasting and to help in communication which are known as artificial satellites, for example, Aryabhata, Rohini etc.
Stars and Planets
A star is a huge ball of hot gases. It gives out heat and light. Planets do not have any or light of their own. They appear bright because they reflect the light of the stars. They revolve around stars.
The sun is actually a star because it has its own heat and light. It is a huge sphere of hot gases. The earth and other seven planets that revolve around the sun get heat and from the sun.
The sun is the main source of energy in our solar system. The planet Mercury is closest to the sun, followed by Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. They revolve around the sun in fixed path called orbit. Stars are far apart from each other.
Distance between stars is measured in light years. The distance travelled by light in year is called light year.
The planets also rotate on their axis. Most of the planets have satellites. A satellite heavenly body that revolves around planets. It does not have any light of its own. The moon is a natural satellite of the Earth 3l shines as it reflects sunlight from its surface. The moon does not have an atmosphere to protect it from extreme heat or cold. Some satellites in the sky are artificial. They have been sent up by scientists of different countries to study space, to forecast weather help in communication. The first one of these was Sputnik 1. Some others are Aryabhata, Rohini, INSAT, etc.
The sun and the eight planets belong to a family called solar system. The eight planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. All of them revolve in fixed path called orbit. Planets rotate on their axis also. Most planets have their satellites which revolve around them. Satellite does not have its own light. Man has also made ne satellites for weather forecasting and to help in communication which are known as artificial satellites, for example, Aryabhata, Rohini etc.
Stars and Planets
A star is a huge ball of hot gases. It gives out heat and light. Planets do not have any or light of their own. They appear bright because they reflect the light of the stars. They revolve around stars.
The sun is actually a star because it has its own heat and light. It is a huge sphere of hot gases. The earth and other seven planets that revolve around the sun get heat and from the sun.
The sun is the main source of energy in our solar system. The planet Mercury is closest to the sun, followed by Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. They revolve around the sun in fixed path called orbit. Stars are far apart from each other.
Distance between stars is measured in light years. The distance travelled by light in year is called light year.
The planets also rotate on their axis. Most of the planets have satellites. A satellite heavenly body that revolves around planets. It does not have any light of its own. The moon is a natural satellite of the Earth 3l shines as it reflects sunlight from its surface. The moon does not have an atmosphere to protect it from extreme heat or cold. Some satellites in the sky are artificial. They have been sent up by scientists of different countries to study space, to forecast weather help in communication. The first one of these was Sputnik 1. Some others are Aryabhata, Rohini, INSAT, etc.
 (a) 4,125 (b) 1,125
(c) 3,243 (d) 1,243
(e) None of these
Answer (b)
Explanation: Here, pattern followed is:
(a) 4,125 (b) 1,125
(c) 3,243 (d) 1,243
(e) None of these
Answer (b)
Explanation: Here, pattern followed is:
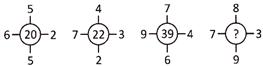 (a) 31 (b) 28
(c) 27 (d) 29
(e) 26
Answer (d)
Explanation: Here, rule followed is:
(a) 31 (b) 28
(c) 27 (d) 29
(e) 26
Answer (d)
Explanation: Here, rule followed is:
 Paleontologists study fossils to understand how a plant or an animal has changed over the year. They do this by comparing the fossils to what is alive today. But some plants and animals, like the dinosaurs, are not alive today. That makes a paleontologist's job extremely difficult. They have to make sense out of a fossil in much the same way as you would with a jigsaw puzzle. To do this, they also need to understand whether the rocks were formed under the sea or land. They are experts at telling the age of rocks.
If you decide to become a paleontologist, you would be of great help to your country in locating oil reservoirs. Oil is often found in rocks that contain certain fossils. Oil companies use such fossils as clues to locate oil reservoirs.
1. Pre-historic times are ________.
(a) times more than 4,500 years ago
(b) times more than 5,500 years ago
(c) times less than 4,500ryears ago
(d) times less than 5,500 years ago
(e) None of these
2. more...
Paleontologists study fossils to understand how a plant or an animal has changed over the year. They do this by comparing the fossils to what is alive today. But some plants and animals, like the dinosaurs, are not alive today. That makes a paleontologist's job extremely difficult. They have to make sense out of a fossil in much the same way as you would with a jigsaw puzzle. To do this, they also need to understand whether the rocks were formed under the sea or land. They are experts at telling the age of rocks.
If you decide to become a paleontologist, you would be of great help to your country in locating oil reservoirs. Oil is often found in rocks that contain certain fossils. Oil companies use such fossils as clues to locate oil reservoirs.
1. Pre-historic times are ________.
(a) times more than 4,500 years ago
(b) times more than 5,500 years ago
(c) times less than 4,500ryears ago
(d) times less than 5,500 years ago
(e) None of these
2. more... You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
