 Her mom gave her another fish on her birthday.
Her mom gave her another fish on her birthday.
 How many fish are there in all?
There was 1 fish in the fish tank. One more is added to it.
Therefore, total number of fish in the fish tank = 1 + 1 = 2
How many fish are there in all?
There was 1 fish in the fish tank. One more is added to it.
Therefore, total number of fish in the fish tank = 1 + 1 = 2
 There were 9 mangoes on the tree. Monty could not get any mango. It means still there were 9 mangoes on the tree.
This can be written as 9 – 0 = 9
Therefore, there were 9 mangoes left on the tree.
Hence, we can say that when we subtract zero from a number, the answer is the number itself.
SUBTRACTION WITH NUMBER LINE
72 – 45 =?
There were 9 mangoes on the tree. Monty could not get any mango. It means still there were 9 mangoes on the tree.
This can be written as 9 – 0 = 9
Therefore, there were 9 mangoes left on the tree.
Hence, we can say that when we subtract zero from a number, the answer is the number itself.
SUBTRACTION WITH NUMBER LINE
72 – 45 =?
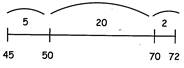 5 + 20 + 2 = 27
Therefore, 72 - 45 = 27
USES OF SUBTRACTION
5 + 20 + 2 = 27
Therefore, 72 - 45 = 27
USES OF SUBTRACTION

 Therefore, number of students left unselected = Total number of students - Number of students selected = 75 - 25 = 50 more...
Therefore, number of students left unselected = Total number of students - Number of students selected = 75 - 25 = 50 more...  She wants to give 6 sweets to each family. She started counting the number of sweets to be purchased from the market.
She wants to give 6 sweets to each family. She started counting the number of sweets to be purchased from the market.  She finds it quite difficult and time consuming to count the total number of sweets to be purchased. Can you help her find out an easier way to do so?
6 sweets are to be distributed to each family and there are 20 families in all. So instead of adding 6 again and again 20 times, we can simply multiply 6 by 20. The answer will be the same in both the cases.
6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 +
6 + 6 + 6 + 6 = \[6\times 20=120\] sweets.
Therefore, we can say that multiplication is a short form of repeated addition.
It is a mathematical operation that indicates how many times a number is added to itself.
Multiplication is the process of finding the product of any two numbers.
TERMINOLOGY
When multiplication is considered as repeated addition:
She finds it quite difficult and time consuming to count the total number of sweets to be purchased. Can you help her find out an easier way to do so?
6 sweets are to be distributed to each family and there are 20 families in all. So instead of adding 6 again and again 20 times, we can simply multiply 6 by 20. The answer will be the same in both the cases.
6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 +
6 + 6 + 6 + 6 = \[6\times 20=120\] sweets.
Therefore, we can say that multiplication is a short form of repeated addition.
It is a mathematical operation that indicates how many times a number is added to itself.
Multiplication is the process of finding the product of any two numbers.
TERMINOLOGY
When multiplication is considered as repeated addition:
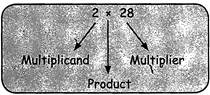 The, number to be multiplied is called the multiplicand. The number of multiples is called the multiplier. When any two numbers are multiplied: The numbers to be multiplied are called factors or multiplicands.
The, number to be multiplied is called the multiplicand. The number of multiples is called the multiplier. When any two numbers are multiplied: The numbers to be multiplied are called factors or multiplicands.
 The result after multiplication is known as the product.
PROPERTIES OF MULTIPLICATION
The result after multiplication is known as the product.
PROPERTIES OF MULTIPLICATION
 Amazing Facts
Multiplying two same numbers with 5 at ones place.
Example, \[45\times 45=?\]
The last two digits of the answers will always be 25.
Now multiply 4 by the number that follows it i.e.
\[5.\left( 4\times 5=20 \right)\]
Write the number in front of 25. \[\underline{2025}\]
Therefore, \[45\times 45=2025\]
Multiplying by 11.
For multiplying any number by 11, just place the first and last digit as it is on their respective places and add the two digits and place the sum between the first and last digit.
Example,
Th H T more...
Amazing Facts
Multiplying two same numbers with 5 at ones place.
Example, \[45\times 45=?\]
The last two digits of the answers will always be 25.
Now multiply 4 by the number that follows it i.e.
\[5.\left( 4\times 5=20 \right)\]
Write the number in front of 25. \[\underline{2025}\]
Therefore, \[45\times 45=2025\]
Multiplying by 11.
For multiplying any number by 11, just place the first and last digit as it is on their respective places and add the two digits and place the sum between the first and last digit.
Example,
Th H T more... 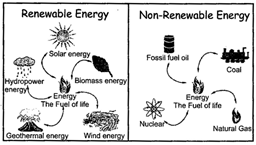 The goal in using renewable energy sources is to reduce the negative environmental effects associated with non-1 renewable energy sources such as coal and natural gas. Opting to use a renewable energy source is cost- effective? And also helps protect the environment from the risks of fossil fuel emissions of non-renewable energy sources.
Historical Preview
In the beginning, the sun was the only source of energy. People would gather food during the day, and when the sun went down at night, they would search for shelter from the cold. Eventually someone discovered fire more...
The goal in using renewable energy sources is to reduce the negative environmental effects associated with non-1 renewable energy sources such as coal and natural gas. Opting to use a renewable energy source is cost- effective? And also helps protect the environment from the risks of fossil fuel emissions of non-renewable energy sources.
Historical Preview
In the beginning, the sun was the only source of energy. People would gather food during the day, and when the sun went down at night, they would search for shelter from the cold. Eventually someone discovered fire more...  Example: walking, talking, swallowing, taste and smell etc all are regulated by our brain. In short we can say anything we do, our brain is involved in it.
4. Teeth and its functions: We have two sets of teeth during our lifetime; they are milk teeth/deciduous. Teeth and permanent teeth. There are altogether 20 deciduous teeth and 32 permanent teeth.
Enamel
Transparent or milky white colour.
The hardest tissue in a human body (harder than bone)
Dentine
Slightly yellowish in colour
Pulp
Filled with blood vessels and nerve fibres.
We have different types of deciduous teeth: incisors canines, first molars, and second molars. Incisor - to cut food like a pair of scissors. Canine - to tear food like a fork. First molars - can grind food. Second molar – larger than first molars, can grind food like first molars do.
FUNCTIONS OF TEETH
Food needs more...
Example: walking, talking, swallowing, taste and smell etc all are regulated by our brain. In short we can say anything we do, our brain is involved in it.
4. Teeth and its functions: We have two sets of teeth during our lifetime; they are milk teeth/deciduous. Teeth and permanent teeth. There are altogether 20 deciduous teeth and 32 permanent teeth.
Enamel
Transparent or milky white colour.
The hardest tissue in a human body (harder than bone)
Dentine
Slightly yellowish in colour
Pulp
Filled with blood vessels and nerve fibres.
We have different types of deciduous teeth: incisors canines, first molars, and second molars. Incisor - to cut food like a pair of scissors. Canine - to tear food like a fork. First molars - can grind food. Second molar – larger than first molars, can grind food like first molars do.
FUNCTIONS OF TEETH
Food needs more...  SUN
SUN
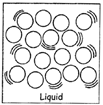
 LIQUID
LIQUID
 GASES
GASES
 Amazing Facts
Glass is actually a liquid; it just flows very, very slowly.
Liquid oxygen is blue.
Hot water freezes quicker than cold water
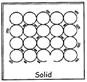
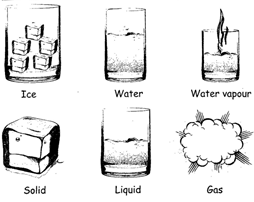
CHANGE OF STATE
Matters can be changed from one state to another state. A solid can be changed into liquid and a liquid can be changed into gas. Most of the metals, which ore solid, turn into liquid on heating and turn into vapour on further heating.
Amazing Facts
Glass is actually a liquid; it just flows very, very slowly.
Liquid oxygen is blue.
Hot water freezes quicker than cold water
CHANGE OF STATE
Matters can be changed from one state to another state. A solid can be changed into liquid and a liquid can be changed into gas. Most of the metals, which ore solid, turn into liquid on heating and turn into vapour on further heating.
 more...
more... You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
