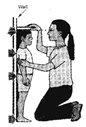
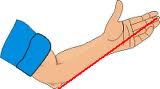
 Cubit Hand span
The metre is what we normally use for measuring lengths. Smaller lengths an measured in centimetres. Metre is written as m and centimetre as cm.
Measurement of Mass
Mass tells us how heavy or light an object is. We use weighing scales to find the mass of an object.
Just as we use metre for measuring length, we use kilogram for measuring mass. Smaller weights are measured in grams. Kilogram is written as kg and gram is written as g.
Cubit Hand span
The metre is what we normally use for measuring lengths. Smaller lengths an measured in centimetres. Metre is written as m and centimetre as cm.
Measurement of Mass
Mass tells us how heavy or light an object is. We use weighing scales to find the mass of an object.
Just as we use metre for measuring length, we use kilogram for measuring mass. Smaller weights are measured in grams. Kilogram is written as kg and gram is written as g.


 Mars has a lower gravity than Earth, therefore a person weighing 100 kg (220 pounds) on Earth would only weigh 38kg (84 pounds) on Mars.
Only one third of the energy in burning coal reaches the consumer as electricity.
If 10,000 schools turned off their lights for one minute it could save $81,885.
Mars has a lower gravity than Earth, therefore a person weighing 100 kg (220 pounds) on Earth would only weigh 38kg (84 pounds) on Mars.
Only one third of the energy in burning coal reaches the consumer as electricity.
If 10,000 schools turned off their lights for one minute it could save $81,885.

 Plant Kingdom Animal Kingdom
The plant kingdom comprises of all the green plants present on the land, water and even those which are non-green in colour. The green colour of the plant is due to the presence of chlorophyll, which aid in photosynthesis. Nature has a wide variety of plants. Each variety has its own uniqueness. We see most of the plant that are green. But there are plants which has coloured leaves. Flowers of some are huge, while some have tiny one. Yet another group doesn't have any flower at all. Some plants have thorns while some are soft, delicate, beautiful and great to smell. We can also see plant life in and on water. Some plants live in dry places, while others need maximum rainfall.
Plant Kingdom Animal Kingdom
The plant kingdom comprises of all the green plants present on the land, water and even those which are non-green in colour. The green colour of the plant is due to the presence of chlorophyll, which aid in photosynthesis. Nature has a wide variety of plants. Each variety has its own uniqueness. We see most of the plant that are green. But there are plants which has coloured leaves. Flowers of some are huge, while some have tiny one. Yet another group doesn't have any flower at all. Some plants have thorns while some are soft, delicate, beautiful and great to smell. We can also see plant life in and on water. Some plants live in dry places, while others need maximum rainfall.
 Plants as Autotrophs
Sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms. Autotrophs can capture the energy of the sunlight to synthesize food. It is a unique process. The survival of almost all living organisms directly or indirectly depends on the food made by the plants. Autotrophs are fundamental to all in the food chains. All animals, almost all fungi, as well as most bacteria and protozoa, depend on autotrophs for the energy and raw materials.
Plants as Autotrophs
Sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms. Autotrophs can capture the energy of the sunlight to synthesize food. It is a unique process. The survival of almost all living organisms directly or indirectly depends on the food made by the plants. Autotrophs are fundamental to all in the food chains. All animals, almost all fungi, as well as most bacteria and protozoa, depend on autotrophs for the energy and raw materials.

 Coleus plant
Coleus plant obtain its food by which one of the following process?
(a) Evaporation
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Transpiration
(d) All of these
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)
Coleus plant
Coleus plant obtain its food by which one of the following process?
(a) Evaporation
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Transpiration
(d) All of these
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)


 (a) Stem
(b) Stomata
(c) Fruit
(d) Flower
(e) Root
Answer: (b)
(a) Stem
(b) Stomata
(c) Fruit
(d) Flower
(e) Root
Answer: (b)
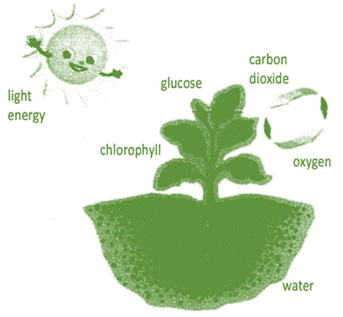 Plants, like other living things use atmospheric oxygen to breakdown glucose (food produced in photosynthesis) into carbon dioxide and water for the release of energy. This energy is used for its growth and maintenance. In plants, all living cells of root, stem and leaf take in oxygen independently and give out carbon dioxide and water. Hence in plants, there is little transport of gases, from one part to another, occurs Respiration in plants occur at a much slower rate as compared to animals.
Plants, like other living things use atmospheric oxygen to breakdown glucose (food produced in photosynthesis) into carbon dioxide and water for the release of energy. This energy is used for its growth and maintenance. In plants, all living cells of root, stem and leaf take in oxygen independently and give out carbon dioxide and water. Hence in plants, there is little transport of gases, from one part to another, occurs Respiration in plants occur at a much slower rate as compared to animals.  Water Hyacinth
Water Hyacinth
 Lotus Plant
Lotus Plant
 Pond Weed
Pond Weed

 Non-Green Plant
Non-Green Plant



 Pine tree Deodar tree Lichens
Pine tree Deodar tree Lichens


 Mango tree Pipal tree Ashok tree
Mango tree Pipal tree Ashok tree


 Tea Plants Coffee Plant Rubber Plant
Tea Plants Coffee Plant Rubber Plant
| more...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to:—
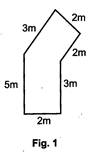 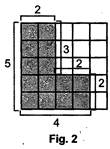 Here, each square is of side 1 unit.
Perimeter of shaded region
= 2 units + 5 units + 4 units + 2 units + 2 units
+ 3 units = 18 units
Here, each square is of side 1 unit.
Perimeter of shaded region
= 2 units + 5 units + 4 units + 2 units + 2 units
+ 3 units = 18 units
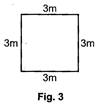 = Sum of the sides of the square
= 3m + 3m + 3m + 3m or
\[=4\times 3m=12m\]
Thus, perimeter of a square = 4 x side
Perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of the length of its sides.
= Sum of the sides of the square
= 3m + 3m + 3m + 3m or
\[=4\times 3m=12m\]
Thus, perimeter of a square = 4 x side
Perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of the length of its sides.
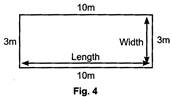 Perimeter of rectangle in fig. 4
= sum of the sides of the rectangle
\[=3m+10m+3m+10m\]or
\[=(3m+3m)+(10m+10m)\]
\[=(2\times 3m)+(2\times 10m)\]
\[=2\times (3m+10m)\]
\[=2\times (13m)=26\text{ }m\]
Thus, perimeter of a rectangle = 2 x (length + width)
Perimeter of a circle is the distance around the circle.
Perimeter of rectangle in fig. 4
= sum of the sides of the rectangle
\[=3m+10m+3m+10m\]or
\[=(3m+3m)+(10m+10m)\]
\[=(2\times 3m)+(2\times 10m)\]
\[=2\times (3m+10m)\]
\[=2\times (13m)=26\text{ }m\]
Thus, perimeter of a rectangle = 2 x (length + width)
Perimeter of a circle is the distance around the circle.
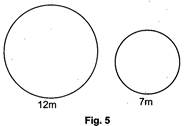 Also, perimeter of a circle is known as circumference of it.
Amazing Facts
Also, perimeter of a circle is known as circumference of it.
Amazing Facts
Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. |