Category : 11th Class
![]()
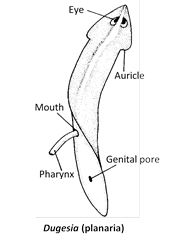
(1) Dugesia (Planaria) is found commonly in freshwater ponds, lakes, streams and shallow rivers.
(2) Planaria are gregarious, i.e., they live in groups.
(3) The head bears a pair of lateral projections called auricles.
(4) The mouth opens on the mid ventral surface near the middle of the animal.
(5) The pharynx is a tubular structure that can be everted beyond the mouth.
(6) Planarians have remarkable power of regeneration.
(7) If an individual is cut transversely into two parts, the anterior fragment will regenerate a new tail and a posterior piece will develop a new head.
(8) Neoblast cells found in planarians which is help in regeneration.
![]()
(1) Fasciola hepatica, commonly known as sheep liver fluke is an endoparasite of sheep which reside in the liver and bile duct.
(2) The liver fluke has a dorsoventrally flat, unsegmented body with two suckers, oral sucker (anterior sucker) and acetabulum (ventral sucker).
(3) Liver fluke is covered with a cuticle, lacks ciliated epidermis.
(4) There are three parmanent apertures on the body-mouth (surrounded by oral sucker), genital pore (located between the two suckers), excretory pore (At the extreme posterior end). During breeding season a temporary opening, the aperture of laurer’s canal is also developed. Laurer’s canal is present between the genital aperture and the uterus.
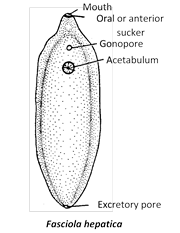
(5) Suctorial pharynx with bifurcated intestine. A large number of caeca or diverticulae arise from each branch of intestine.
(6) Digestion is holozoic. The parasite obtains nourishment from bile, blood, lymph and epithelial cells.
(7) Respiration is anaerobic.
(8) Excretion occurs with the help of flame cells.
(9) Fasciola is a digenetic endoparasite which are its primary host is sheep causing ‘liver rot’ and the secondary or intermediate host is the snail of genus Limnaea and Planorbis.
(10) Fasciola hepatica is a hermaphrodite. In male has a pair of testes and female has an ovary, vitteline gland for yolk formation and mehlis’s gland for lubrication.
(11) Fertilization is internal. Cross fertilization commonly occurs.
(12) Different larval stages of Fasciola hepatica according to development sequence are : miracidium-sporocyst-Redia-Cercaria-Metacercaria.
(13) Stage in the life cycle of Fasciola when it infects intermediate host (snail) is miracidium and primary host is metacercaria.
(14) Miracidium and cercaria larva are free swimming form in water. Redia and sporocyst are formed in snail.
(15) Fasciola exhibits both alternation of generation and alternation of host.
![]()
(1) Schistosoma is commonly known as human blood fluke and it is found in the blood vesseles and hepatic portal system of man, cat, pig, dog, etc.
(2) Phenomenon of sexual dimorphism occurs. Thus male and female are separate but they live in close association.
(3) Male is flattened while female is slender. Both possess oral and ventral suckers.
(4) The ventral folding from the male’s body forms a groove known as ‘Gynecophoric canal’ in which the female individual lives.
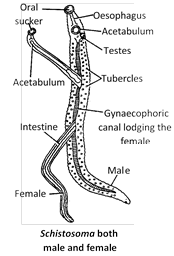
(5) Blood fluke feeds on blood. It respires anaerobically. Excretion occurs with the help of flame cells.
(6) Blood fluke is digenetic, primary host is man and secondary host snail.
(7) Fertilization is internal. After fertilization the egg developed into miracidium larva which is free swimming. Later on it penetrates snail body and get converted into cercaria larva. The cercaria infect man by penetrating his skin.
(8) Redia and metacercaria stage do not occurs in blood fluke.
(9) Blood fluke causes schistosomiasis or bilharzia.
![]()
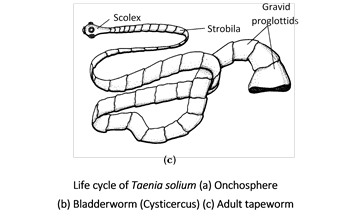
(1) Taenia solium is commonly known as pork-tape-worm.
(2) Adult tapeworm lives in the small intestine of man (primary host), larval stage in the secondary or intermediate host pig or cattle.
(3) Taenia solium possesses elongated ribbon or tape like segmented body (pseudometamerism).
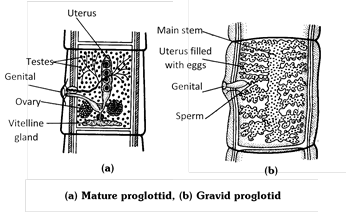
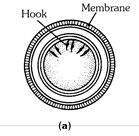
(4) Body is divided into three parts, namely scolex, neck and strobila. Scolex has a rostellum bearing two circles of chitinous hooks and four suckers for holding onto the host. Neck is the region of proliferation of new proglottids. Strobila is long tapering part having large number of proglottids. Proglottids are of three types-young, mature and gravid.
(5) Young or immature proglottids are behind neck without reproductive organs.
(6) Mature proglottids are in the middle having reproductive organs, both male and female.
(7) Gravid proglottids (rectangular in shape) are with branched uterus containing fertilized eggs.
(8) Apolysis is the process of separation of gravid proglottids.
(9) Body wall lacks a cellular epidermis. It consists of cuticle (parasitic adaptation), musculature and mesodermal tissue called parenchyma.
(10) Digestive system is simple without alimentary canal. Food is absorbed through body surface.
(11) Respiration is anaerobic in Taenia solium.
(12) Flame-cells (solenocytes) are excretory in function.
(13) All tapeworms are hermaphrodites, and a complete reproductive system occurs in each mature proglottid. Fertilization is internal, cross type within the same proglottid or between two proglottids of the same strobilla.
(14) The fertilised eggs develop into an embryo that gets covered by a shell. The shelled embyros are called onchospheres. Secondary host pig acquires infection by ingesting the onchospheres. Hexacanth is developed in shell with six hooks.
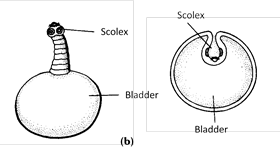
(15) Hexacanth stage is the infective stage to pig. In the stomach of pig, hexacanth will be released, it goes through blood circulation and on reaching muscles get encysted in the form of bladderworm (cysticercus). Human host gets infection by eating raw or poorly cooked ‘measly pork’. Cysticercus is infective stage to man.
(16) Cysticerci in pig muscle can remain viable for several years.
(17) Taenia saginata (Taeniarhynchus saginatus) is commonly known as ‘the beef tapeworm’.
(18) Like Taenia solium, it is digenetic, man is the primary host and cattle is the intermediate host.
(19) It is also called ‘unarmed tapeworm’ because the scolex does not possess hooks.
(20) During infection taenia necrosis of brain and epilepsy may appear.
(21) The disease caused by bladderworm is known as cysticercosis. Cysticercosis is more dangerous than taeniasis.
Common Names
|
Fasciola hepatica - Sheep liver fluke Fasciola gigantica - Cattle liver fluke Schistosoma mansoni - Human blood fluke Fasciolopsis buski - Intestinal fluke Paragonimus westermani - Lung fluke Taenia solium - Pork tapeworm Taenia saginata - Beef tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus - Dog tapeworm |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
