Category :
10th Class
Money and Credit
IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS
- Money is the most basic and significant invention of mankind. Money occupies a unique position in a modem economy. In its absence the whole prosperous economic life would collapse like a pack of cards.
| Definition. Money may be defined as anything which is generally accepted by the people in exchange of goods and services or in repayment of debts. According to Crowther, "Money can be defined as anything that is generally accepted as a means of exchange and at the same time acts as a measure and as a store of value." |
- Barter Exchange/Barter System. It implies direct exchange of goods against goods without use of money is called barter exchange. It is also called C.C. economy, i.e., commodity for commodity exchange economy. When a weaver gives cloth to the farmer in return for getting wheat from the farmer, this is called barter exchange.
- Inconveniences of Barter Exchange.
| (a) Lack of double coincidence of wants. |
| (b) Absence of common measure of value. |
| (c) Lack of divisibility. |
| (d) Difficulty in storing wealth. |
| (e) Lack of satisfactory unit to engage in contracts. |
- Functions of Money.
| (a) Medium of Exchange |
| (b) Measure of Value |
| (c) Standard of Demand Payments |
| (d) Store of Value. |
- Money as a Legal Tender Money. Currency (coins and notes) is a legal tender money which cannot be refused in payment for transactions- Everybody is bound to accept it in exchange for goods and services and in discharge of debts. None can refuse to accept it because non-acceptance is an offence. It is issued by the government or duly authorised Central Bank.
- Demand Deposits. Deposits in a bank which are payable on demand are called demand deposits. It also provides the facility of medium of exchange which is a function of money, when payments are made by cheques.
- Cheque. It is a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person's account to the person in whose name the cheque has been made.
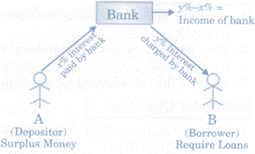
- Loan Activities of Banks. Basically banks borrow money to lend. Banks pay interest (suppose x %) from whom it borrows. After keeping a portion of deposits as reserves, banks lend to people who demand money as loan and bank charges interest (suppose y %} from them. The difference between what is charged from borrowers y %) and what is paid to depositors is their main sources of income. After meeting all expenses of banks out of this income, the resultant is profit/loss for the bank.
- Credit (loan).it plays a vital and positive role in economic life. Money/finance is very important for a firm or organisation just like air in the balloon. Credit (loan) refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment. Main demand for credit is for crop production in case of rural areas.
- Debt-trap. Suppose a person takes a loan and due to unavoidable circumstances he is not able to repay his loan. Now he faces a difficult situation and has to take a tough decision, either he has to borrow a fresh loan or sell some part of his property to repay the earlier loan.
- Terms of Credit. It includes details regarding interest rate, collateral and documentation requirement, and the mode of payment.
- Formal Sector Credit in India. It includes loans from banks and cooperatives. RBI supervises their functions of giving loans. Rich urban households depend largely on formal sources of credit. Lower rate of interest on loans is charged as compared to informal sources of credit.
- Informal Sector Credit in India. It includes traders, employers, moneylenders, relatives, friends, etc. No organisation is there to supervise its lending activities, Higher interest on loans is charged as compared to formal sources of credit. Poor households largely depend on informal sources of credit.
- Self Help Groups (SHG) for the Poor. It helps in pooling the savings of the members, who are poor women. Members can get timely loans for a variety of purposes and at a reasonable rate of interest. It helps borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral. It also provides a platform to discuss variety of social issues of their concern.
- Chit Fund. Chit means a transaction under which a person enters into an agreement with a specified number of persons that every one of them shall subscribe a certain amount of money by way of periodic instalments over a definite period. Reasonable rate of interest is charged against the loan taken by subscriber members.

