REAL NUMBER
FUNDAMENTALS
- Rational numbers: Numbers which can be written in the form of\[\frac{p}{q}(q\ne 0)\], where p and q are integers, are called rational numbers.
Note: Every terminating decimal and non-terminating repeating decimal can be expressed as a rational number,
- Irrational numbers: Numbers which cannot be written in the form of \[\frac{p}{q}\]where p and q are integers and q ^ 0 are called irrational, numbers. Numbers which are not rational are called irrational numbers.
- Real numbers: The rational numbers and the irrational numbers together are called real numbers. Both rational & irrational numbers real line on number line.
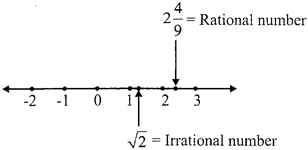
Note: Any number that can be represented on a number line is called a real number.
- Lemma: A proven statement which is used to prove another statement is called a lemma.
- Euclid’s division lemma: For any two positive integers ‘a’ and ‘b’, there exist whole numbers ‘q’ and ‘r’ such that \[a=bq+r,0\le r<b\]
This is an extension of the idea:
Dividend = Divisor x quotient + Remainder
(a) (b) (q) (r)
Remainder ‘r’ is always less than divisor (b) (This is basic principle of mathematics).
Note: Euclid’s division algorithm is stated only for positive integers, but can be extended/or all negative integers.
- Algorithm: An algorithm is a process of solving particular problems.
- Euclid’s division algorithm is used to find the Highest Common Factor (H.C.F.) of two numbers.
- Following is the procedure for finding H.C.F. using Euclid’s division algorithm: Suppose the two positive numbers are ‘a’ and ‘b’, such that a > b. Then the H.C.F. of ‘a’ and ‘b’ can be found by following the steps given.
(a) Apply the division lemma to find ‘q’ and ‘r’ where \[a=bq+r,0\le r<b\].
(b) If r = 0, then\[H.C.F.\,\,is\,\,b.\,\,If\,\,r\ne 0\], then apply Euclid's lemma to find ‘b’ and ‘r’.
- Continue steps (a) and (b) till r = 0. The divisor at this state will be H.C.F. (a, b). Also, H.C.F. (a, b) = H.C.F. (b, r).
- Fundamental theorem of Arithmetic: Every composite number can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers. This is also called the prime factorization theorem.
Note: (i) The order in which the prime factors occur is immaterial.
In general, any composite number x, can be expressed as a product of prime numbers
Elementary Question: 1
Find HCF of 6 and 16.
Also verify that HCF of 18 and 48 is 3 times HCF of 6 and 16.
Sol.: 6 and 16: \[6=2\times 3\]
\[16=2\times 2\times 2\times 2\text{ }\therefore {{\left( HCF \right)}_{1}}=2\]
- and 48: \[18=2\times 3\times 3;\] \[48=2\times 2\times 2\times 2\times 3\]
\[\therefore {{(HCF)}_{2}}=2\times 3=6;\] \[\therefore {{\left( HCF \right)}_{2}}=\text{ }3\times {{\left( HCF \right)}_{1}}\]
Elementary Question: 2
Do the above problem by Euclid is division algorithm.
- C.M. of \[\frac{a}{b}\] and \[\frac{c}{d}=\frac{L.C.M.\,\,of\,\,a\,\,and\,\,c}{H.C.F.\,\,of\,\,b\,\,and\,\,d}=\frac{L.C.M.\,\,(a,c)}{H.C.F.\,\,(b,d)}.\]
- Some Important Result on Natural Numbers
more...
 Green revolution
Green revolution
 White Revolution
White Revolution
 Chapter Coverage
Chapter Coverage

 Chapter Coverage
Chapter Coverage
 Important Terms And Concepts
Important Terms And Concepts
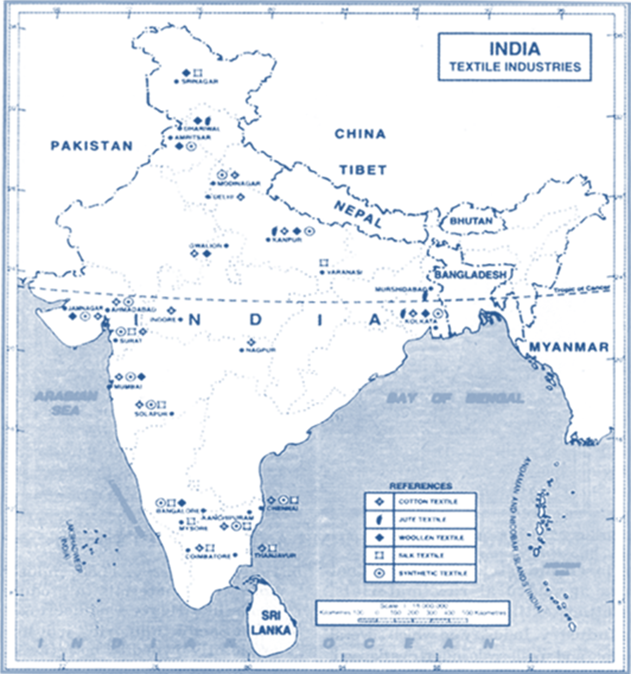 Chapter Coverage
Chapter Coverage
 Chapter coverage
· Resources
· Classification of Resources
· Development of Resources
· Resource Planning
· Conservation of Resources
· Land Resources
· Land Use Pattern
· Land Degradation and Conservation Measures
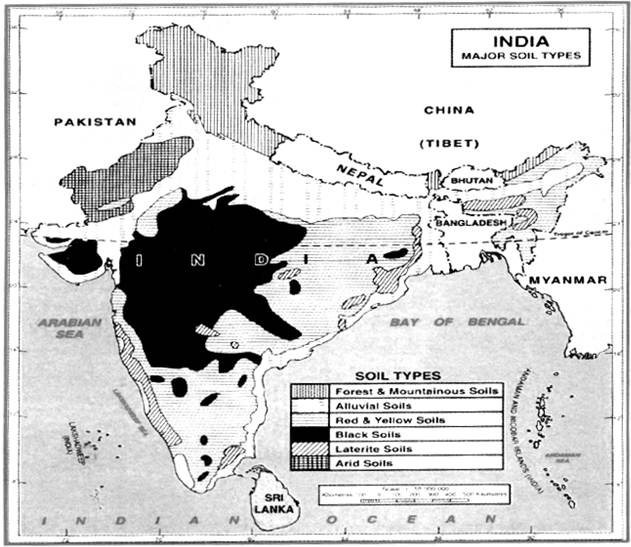
· Soil
· Types of Soils
· Soil Erosion
· Soil Conservation
· Map Work
Chapter coverage
· Resources
· Classification of Resources
· Development of Resources
· Resource Planning
· Conservation of Resources
· Land Resources
· Land Use Pattern
· Land Degradation and Conservation Measures
· Soil
· Types of Soils
· Soil Erosion
· Soil Conservation
· Map Work 
 Note: Any number that can be represented on a number line is called a real number.
Note: Any number that can be represented on a number line is called a real number.