 CHAPTER COVERAGE
CHAPTER COVERAGE
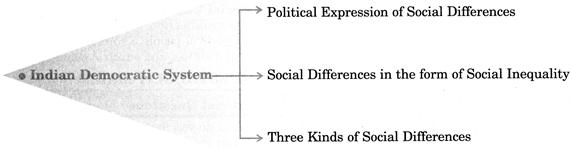
 CHAPTER COVERAGE
CHAPTER COVERAGE
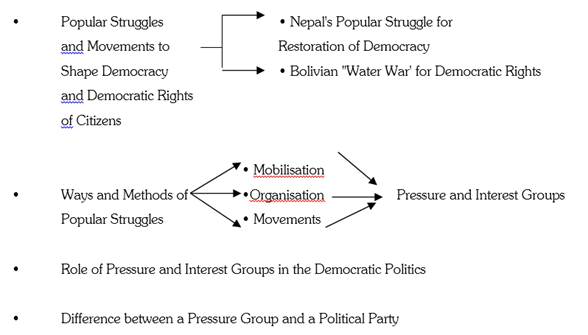

 Chapter Coverage
Chapter Coverage

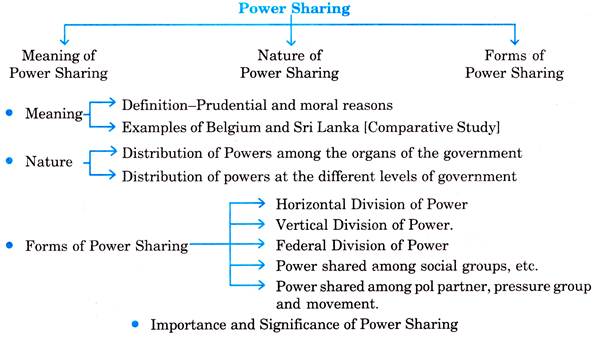

 Chapter Coverage
Chapter Coverage
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
